Fill Out a Valid Bill of Lading with a Supplement Form
The Bill of Lading with a Supplement form plays a crucial role in the transportation and shipping industry, serving as a vital document that facilitates the movement of goods. This form not only acts as a receipt for the merchandise but also outlines the terms and conditions under which the goods are transported. It includes essential information such as the names and addresses of the shipper and consignee, a detailed description of the cargo, and any special instructions pertinent to the shipment. The supplement portion of the form allows for additional clauses or conditions that may be necessary for specific transactions, ensuring that all parties involved have a clear understanding of their rights and responsibilities. This document also serves as a contract between the carrier and the shipper, establishing the legal framework for the transportation process. By incorporating both standard and supplementary provisions, the Bill of Lading with a Supplement form aims to protect the interests of all stakeholders while promoting efficiency and clarity in the shipping process. Understanding this form is essential for anyone involved in the logistics and supply chain management, as it lays the foundation for successful commercial transactions.
Common mistakes
When filling out a Bill of Lading with a Supplement form, individuals often encounter various pitfalls. These mistakes can lead to delays, additional costs, or even legal complications. Below is a list of common errors to avoid:
- Incomplete Information: Failing to provide all required details can result in processing delays. Ensure every section is filled out completely.
- Incorrect Item Descriptions: Mislabeling items or using vague descriptions can lead to confusion. Be specific about the nature of the goods being transported.
- Omitting Weight and Dimensions: Not including accurate weight and dimensions can affect shipping costs and logistics. Always double-check these figures.
- Wrong Consignee Information: Providing incorrect details for the recipient can cause delivery issues. Verify the consignee's name and address before submission.
- Neglecting Special Instructions: Failing to include special handling instructions may lead to damage or loss. If special care is needed, make it clear.
- Ignoring Legal Requirements: Not being aware of legal obligations related to the shipment can lead to penalties. Familiarize yourself with relevant regulations.
- Forgetting Signatures: Omitting required signatures can render the document invalid. Always ensure that all necessary parties have signed.
- Using Outdated Forms: Submitting an old version of the form can cause confusion. Always use the most current version available.
- Failing to Review: Skipping a final review of the form can lead to overlooked errors. Take the time to check for accuracy before submission.
By being mindful of these common mistakes, individuals can improve their accuracy when completing a Bill of Lading with a Supplement form. This diligence not only facilitates smoother transactions but also fosters better relationships with carriers and clients alike.
Preview - Bill of Lading with a Supplement Form

Date: |
BILL OF LADING |
Page 1 of ______ |
|
SHIP FROM |
|
|
|
Name: |
|
Bill of Lading Number:__________________ |
|
Address: |
|
|
|
City/State/Zip: |
|
|
B A R C O D E S P A C E |
SID#: |
FOB: o |
|
|
SHIP TO |
|
CARRIER NAME: _________________________________ |
|
Name: |
Location #:____ |
||||
Address: |
|
|
|
|
|
City/State/Zip: |
|
|
|
|
|
CID#: |
FOB: |
|
o |
|
|
THIRD PARTY FREIGHT CHARGES BILL TO:
Name:
Address:
City/State/Zip:
SPECIAL INSTRUCTIONS:
Trailer number:
Seal number(s):
SCAC:
Pro number:
B A R C O D E S P A C E
Freight Charge Terms:
Prepaid ________ |
Collect _______ 3rd Party ______ |
oMaster Bill of Lading: with attached
(check box) underlying Bills of Lading
CUSTOMER ORDER NUMBER
# PKGS
CUSTOMER ORDER INFORMATION |
|
||
WEIGHT |
PALLET/SLIP |
|
ADDITIONAL SHIPPER INFO |
|
Y OR N |
|
|
GRAND TOTAL
CARRIER INFORMATION
HANDLING UNIT |
PACKAGE |
||
|
|
|
|
QTY |
TYPE |
QTY |
TYPE |
|
|
|
|
WEIGHT
H.M.
(X)
COMMODITY DESCRIPTION
Commodities requiring special or additional care or attention in handling or stowing must be
so marked and packaged as to ensure safe transportation with ordinary care.
LTL ONLY
NMFC # |
CLASS |
|
|
R E C E I V I N G
S T A M P S P A C E
GRAND TOTAL
Where the rate is dependent on value, shippers are required to state specifically in writing the agreed or |
COD Amount: $____________________ |
|
declared value of the property as follows: |
||
“The agreed or declared value of the property is specifically stated by the shipper to be not exceeding |
Fee Terms: Collect: ¨ |
Prepaid: o |
__________________ per ___________________.” |
Customer check acceptable: o |
|
NOTE Liability Limitation for loss or damage in this shipment may be applicable. See 49 U.S.C. - 14706(c)(1)(A) and (B).
RECEIVED, subject to individually determined rates or contracts that have been agreed upon in writing between the carrier and shipper, if applicable, otherwise to the rates, classifications and rules that have been established by the carrier and are available to the shipper, on request, and to all applicable state and federal regulations.
The carrier shall not make delivery of this shipment without payment of freight and all other lawful charges.
_______________________________________Shipper Signature
SHIPPER SIGNATURE / DATE
This is to certify that the above named materials are properly classified, packaged, marked and labeled, and are in
to certify that the above named materials are properly classified, packaged, marked and labeled, and are in proper condition for transportation according to the applicable regulations of the DOT.
proper condition for transportation according to the applicable regulations of the DOT.
Trailer Loaded: Freight Counted:
p By Shipper p
 By Shipper
By Shipper
p
 By Driver p
By Driver p
 By Driver/pallets said to contain
By Driver/pallets said to contain
pBy Driver/Pieces
CARRIER SIGNATURE / PICKUP DATE
Carrier acknowledges receipt of packages and required placards. Carrier certifies emergency response information was made available and/or carrier has the DOT emergency response guidebook or equivalent documentation in the vehicle.
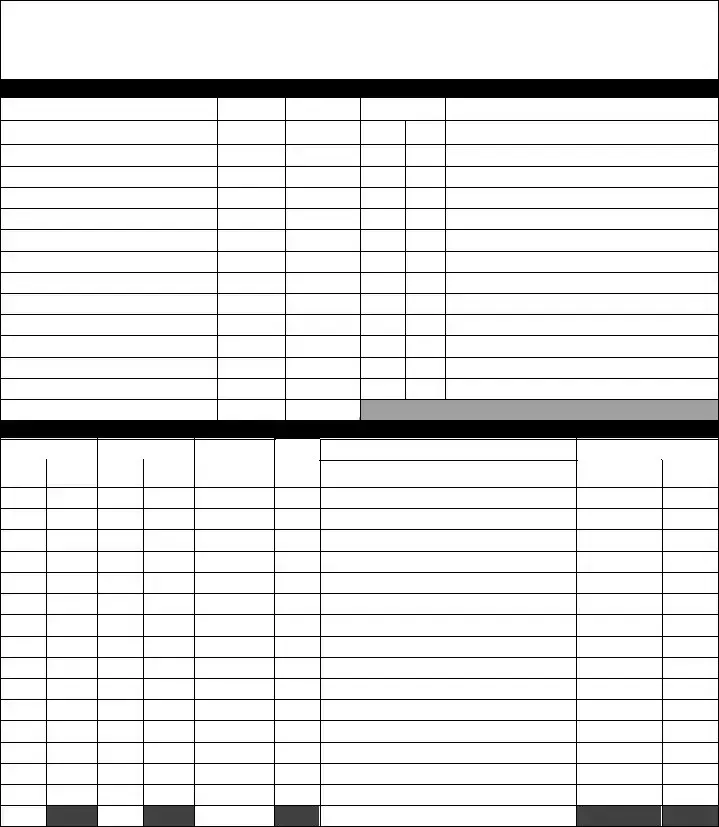
SUPPLEMENT TO THE BILL OF LADING Page _________
Bill of Lading Number: __________________
CUSTOMER ORDER INFORMATION
CUSTOMER ORDER NUMBER # PKGS WEIGHT
PALLET/SLIP
Y OR N
ADDITIONAL SHIPPER INFO
PAGE SUBTOTAL
CARRIER INFORMATION
HANDLING UNIT |
PACKAGE |
|
|
QTY TYPE |
QTY TYPE |
WEIGHT
H.M.
(X)
COMMODITY DESCRIPTION
Commodities requiring special or additional care or attention in handling or stowing must be so marked and packaged as to ensure safe transportation with ordinary care.
LTL ONLY
NMFC # |
CLASS |
PAGE SUBTOTAL
Other PDF Templates
Florida Immunization Registry - The document also serves as proof of immunization for daycare or school enrollments.
Girlfriend Application Funny - Filling out this application can lead to sparks flying in your love life!
For those interested in property transactions, utilizing a smooth process can be advantageous. An informative guide to the use of Quitclaim Deed forms explains how they can facilitate the transfer of ownership seamlessly and with minimal formalities.
What Is Recorded on a Medicine Label Uk - Shows refill history for patient review.
Documents used along the form
The Bill of Lading with a Supplement form is a critical document in the shipping and logistics industry. It serves as a receipt for goods, a contract between the shipper and carrier, and a document of title. However, it is often accompanied by other essential forms and documents that facilitate smooth transactions and ensure compliance with regulations. Below is a list of six commonly used documents in conjunction with the Bill of Lading with a Supplement form.
- Commercial Invoice: This document provides a detailed account of the goods being shipped, including their value, description, and terms of sale. It is crucial for customs clearance and serves as a record for both the buyer and seller.
- Mobile Home Bill of Sale: This document is essential for the transfer of ownership of a mobile home, ensuring proper documentation for the transaction. For more details, you can refer to the Mobile Home Bill of Sale.
- Packing List: The packing list outlines the contents of each package being shipped. It includes details such as item quantities, weights, and dimensions, aiding in inventory management and ensuring that the correct items are delivered.
- Certificate of Origin: This document certifies the country of origin of the goods. It may be required by customs authorities to determine tariff rates and is often necessary for international trade.
- Insurance Certificate: An insurance certificate provides proof that the goods are insured during transit. It protects the shipper and receiver against potential loss or damage, offering peace of mind throughout the shipping process.
- Import/Export License: This license is required for certain goods being imported or exported. It ensures compliance with government regulations and may be necessary to avoid legal issues during the shipping process.
- Customs Declaration: This document is submitted to customs authorities and includes information about the goods being imported or exported. It is essential for assessing duties and taxes and ensuring compliance with trade regulations.
Understanding these documents and their purposes can significantly enhance the efficiency of shipping operations. Proper documentation helps prevent delays, ensures compliance, and fosters trust between parties involved in the shipping process.
Similar forms
The Bill of Lading (BOL) serves as a crucial document in the shipping industry, but it shares similarities with several other important documents. One such document is the Air Waybill (AWB). Both the BOL and AWB function as contracts between the shipper and the carrier. They provide proof of receipt of goods and outline the terms of transportation. However, while a BOL is used for sea freight, an AWB is specifically designed for air transport, reflecting the different modalities of shipping.
Another document similar to the BOL is the Freight Bill. This document details the charges for transportation services provided by the carrier. Like the BOL, the Freight Bill serves as a receipt for the shipment. However, it focuses primarily on the payment aspects rather than the terms of carriage. Both documents are essential for tracking and managing shipping transactions, but they cater to different aspects of the shipping process.
The Commercial Invoice also bears resemblance to the Bill of Lading. This document outlines the sale transaction between the buyer and seller, detailing the goods sold and their value. While the BOL serves as a receipt and a contract of carriage, the Commercial Invoice is critical for customs clearance and payment processing. Both documents are often used together in international shipping to ensure smooth transactions and compliance with regulations.
The Packing List is another document that parallels the BOL. It provides a detailed breakdown of the contents of a shipment, including quantities and descriptions of the items. Like the BOL, the Packing List helps in verifying the goods being shipped. However, it is primarily used for inventory management and does not serve as a contract of carriage. Together, these documents facilitate efficient handling and delivery of goods.
The Certificate of Origin is also similar to the Bill of Lading in that it is often required in international trade. This document certifies the country in which the goods were produced. While the BOL serves as a contract and receipt, the Certificate of Origin is crucial for determining tariffs and trade agreements. Both documents are vital for ensuring compliance with international trade laws.
In the realm of legal documentation, securing a reliable Power of Attorney form is essential for managing affairs effectively. This form allows individuals to designate an agent who can make critical decisions on their behalf, ensuring that their interests are protected during challenging times. To take the first step, fill out the Power of Attorney form by clicking the button below.
Lastly, the Delivery Order shares similarities with the Bill of Lading. The Delivery Order is issued by the consignee or shipper, directing the carrier to release the goods to a specific party. Like the BOL, it acts as a form of authorization for the release of goods. However, the Delivery Order is typically issued after the BOL has been created, serving as a subsequent step in the shipping process.
Dos and Don'ts
When filling out the Bill of Lading with a Supplement form, it's essential to follow specific guidelines to ensure accuracy and compliance. Below is a list of things you should and shouldn't do.
- Do provide complete and accurate information for all fields.
- Do double-check the spelling of names and addresses.
- Do use clear and legible handwriting or type the information.
- Do sign and date the form where required.
- Don't leave any required fields blank.
- Don't use abbreviations that may cause confusion.
- Don't forget to include any additional documents if needed.
- Don't submit the form without reviewing it thoroughly.
Key takeaways
Understanding the Bill of Lading with a Supplement form is essential for anyone involved in the shipping and logistics industry. Here are some key takeaways to consider:
- Purpose: The Bill of Lading serves as a receipt for goods, a contract for transportation, and a document of title.
- Accuracy is Crucial: Ensure all details, such as the shipper's and receiver's information, are accurate to avoid delays.
- Supplement Use: The Supplement form is used to add additional details or amendments to the original Bill of Lading.
- Clear Descriptions: Provide clear and precise descriptions of the goods being shipped to prevent misunderstandings.
- Signatures Matter: Both the shipper and the carrier must sign the Bill of Lading to validate the agreement.
- Retention of Copies: Keep copies of the Bill of Lading and any supplements for record-keeping and potential disputes.
- Legal Implications: Understand that the Bill of Lading is a legally binding document, which can impact liability and claims.
- Tracking Shipments: Use the Bill of Lading to track shipments and confirm delivery status with carriers.
- Compliance: Ensure compliance with all relevant laws and regulations governing the transportation of goods.
How to Use Bill of Lading with a Supplement
Completing the Bill of Lading with a Supplement form is a crucial step in ensuring that your shipment is properly documented. Following these instructions carefully will help you avoid any potential issues during transport.
- Obtain the Form: Start by downloading or printing the Bill of Lading with a Supplement form from the appropriate source.
- Fill in Shipper Information: Enter the name, address, and contact information of the person or company sending the shipment.
- Receiver Information: Provide the name, address, and contact details of the recipient who will receive the shipment.
- Consignee Information: If different from the receiver, fill in the details of the consignee, who is responsible for the goods upon arrival.
- Description of Goods: Clearly describe the items being shipped. Include quantity, weight, and any other relevant details.
- Shipping Instructions: Specify any special instructions for handling or delivering the shipment.
- Payment Terms: Indicate who is responsible for shipping costs. This could be the shipper, receiver, or a third party.
- Sign and Date: The shipper must sign and date the form to validate the information provided.
- Review: Double-check all entries for accuracy before submitting the form.
Once the form is completed, it should be submitted to the carrier along with the shipment. Keep a copy for your records, as it serves as proof of the agreement between you and the carrier regarding the shipment details.
