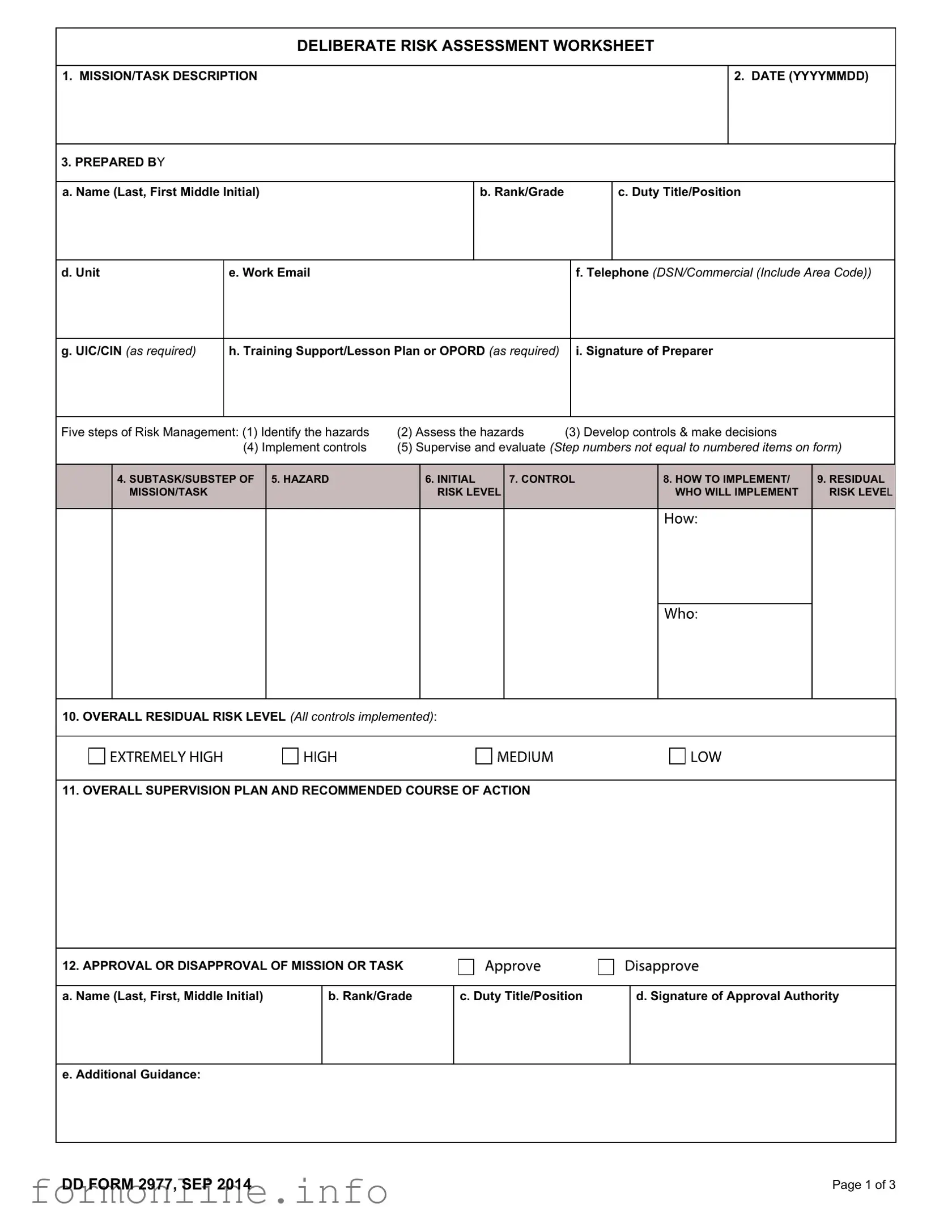
Fill Out a Valid Dd 2977 Form
The DD Form 2977, also known as the Deliberate Risk Assessment Worksheet, plays a crucial role in the risk management process for military operations and training activities. This form is designed to systematically identify, assess, and mitigate risks associated with specific missions or tasks. It requires detailed information, including the mission description, date of preparation, and the individual responsible for completing the form. The form also outlines the five essential steps of risk management: identifying hazards, assessing those hazards, developing controls, implementing those controls, and supervising and evaluating the outcomes. Each section of the form addresses various aspects of risk, such as initial and residual risk levels, and provides a framework for decision-making regarding the approval or disapproval of a mission. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of ongoing risk assessment reviews and encourages feedback and lessons learned to improve future operations. By utilizing the DD Form 2977, military personnel can enhance safety and operational effectiveness through a structured approach to risk management.
Common mistakes
-
Missing Information: One common mistake is failing to complete all required fields. Each section of the DD Form 2977 is important, and missing information can lead to delays or even rejection of the assessment. Ensure that all sections, especially the mission/task description and prepared by fields, are filled out completely.
-
Incorrect Dates: Entering the wrong date format can cause confusion. The form requires dates in the YYYYMMDD format. Double-check that you are using the correct format to avoid any misunderstandings about the timeline of the mission or task.
-
Inaccurate Risk Levels: Misjudging the initial risk level is another frequent error. It's essential to assess both probability and severity accurately using the risk assessment matrix. A miscalculation can lead to inadequate controls being implemented, which could jeopardize safety.
-
Vague Descriptions: Providing vague or overly broad descriptions in the mission/task section can create ambiguity. Be specific about the mission or task and any associated hazards. Clear descriptions help in identifying appropriate controls and actions.
-
Neglecting Feedback: Failing to include a feedback section can overlook valuable lessons learned. After completing the mission or task, it’s crucial to assess what worked and what didn’t. Documenting this information can enhance future risk assessments and improve overall mission success.
Preview - Dd 2977 Form
DELIBERATE RISK ASSESSMENT WORKSHEET
1. MISSION/TASK DESCRIPTION
2. DATE (YYYYMMDD)
3. PREPARED BY
a. Name (Last, First Middle Initial) |
b. Rank/Grade |
c. Duty Title/Position |
d. Unit |
e. Work Email |
|
|
f. Telephone (DSN/Commercial (Include Area Code)) |
|
|
|
|
|
g. UIC/CIN (as required) |
h. Training Support/Lesson Plan or OPORD (as required) |
|
i. Signature of Preparer |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Five steps of Risk Management: (1) Identify the hazards |
(2) Assess the hazards |
(3) Develop controls & make decisions |
||
|
(4) Implement controls |
(5) Supervise and evaluate (Step numbers not equal to numbered items on form) |
||
|
|
|
|
|
4. SUBTASK/SUBSTEP OF 5. HAZARD MISSION/TASK
6.INITIAL RISK LEVEL
7. CONTROL
8.HOW TO IMPLEMENT/ WHO WILL IMPLEMENT
9.RESIDUAL RISK LEVEL
10.OVERALL RESIDUAL RISK LEVEL (All controls implemented):
11.OVERALL SUPERVISION PLAN AND RECOMMENDED COURSE OF ACTION
12. APPROVAL OR DISAPPROVAL OF MISSION OR TASK
a. Name (Last, First, Middle Initial) |
b. Rank/Grade |
c. Duty Title/Position |
d. Signature of Approval Authority |
|
|
|
|
e. Additional Guidance:
DD FORM 2977, SEP 2014 |
Page 1 of 3 |

|
|
Probability (expected frequency) |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Frequent: |
Likely: |
Occasional: |
Seldom: |
Unlikely: |
|
Risk Assessment Matrix |
|
Continuous, |
Several or |
Sporadic or |
Infrequent |
Possible |
|
|
regular, or |
numerous |
intermittent |
occurrences |
occurrences |
||
|
|
inevitable |
occurrences |
occurrences |
|
but improbable |
|
|
|
occurrences |
|
|
|
|
|
Severity (expected consequence) |
|
A |
B |
C |
D |
E |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Catastrophic: Mission failure, unit readiness eliminated; |
I |
EH |
EH |
H |
H |
M |
|
death, unacceptable loss or damage |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Critical: Significantly degraded unit readiness or mission |
II |
EH |
H |
H |
M |
L |
|
capability; severe injury, illness, loss or damage |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Moderate: Somewhat degraded unit readiness or mission |
III |
H |
M |
M |
L |
L |
|
capability; minor injury, illness, loss, or damage |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Negligible: Little or no impact to unit readiness or mission |
IV |
M |
L |
L |
L |
L |
|
capability; minimal injury, loss, or damage |
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Legend: EH - Extremely High Risk H - High Risk M - Medium Risk |
L - Low Risk |
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
13.RISK ASSESSMENT REVIEW (Required when assessment applies to ongoing operations or activities)
a. Date |
b. Last Name |
c. Rank/Grade |
d. Duty Title/Position |
e. Signature of Reviewer |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14. FEEDBACK AND LESSONS LEARNED
15. ADDITIONAL COMMENTS OR REMARKS
DD FORM 2977, SEP 2014 |
Page 2 of 3 |
Instructions for Completing DD Form 2977, "Deliberate Risk Assessment Worksheet"
1.Mission/Task Description: Briefly describe the overall Mission or Task for which the deliberate risk assessment is being conducted.
2.Date (DD/MM/YYY): Self Explanatory.
3.Prepared By: Information provided by the individual conducting the deliberate risk assessment for the operation or training. Legend: UIC = Unit Identification Code; CIN = Course ID Number; OPORD = operation order; DSN = defense switched network; COMM = commercial
4.
5.Hazard: Specify hazards related to the subtask in block 4.
6.Initial Risk Level: Determine probability and severity. Using the risk assessment matrix (page 3), determine level of risk for each hazard specified. probability, severity and associated Risk Level; enter level into column.
7.Control: Enter risk mitigation resources/ controls identified to abate or reduce risk relevant to the hazard identified in block 5.
8.How to Implement / Who Will Implement: Briefly describe the means of employment for each control (i.e., OPORD, briefing, rehearsal) and the name of the individual unit or office that has primary responsibility for control implementation.
9.Residual Risk Level: After controls are
implemented, determine resulting probability, severity, and residual risk level.
10.Overall Risk After Controls are Implemented: Assign an overall residual risk level. This is equal to or greater than the highest residual risk level (from block 9).
11.Supervision Plan and Recommended Course of Action: Completed by preparer. Identify specific tasks and levels of responsibility for supervisory personnel and provide the decision authority with a recommend course of action for approval or disapproval based upon the overall risk assessment.
12.Approval/Disapproval of Mission/Task: Risk approval authority approves or disapproves the mission or task based on the overall risk assessment, including controls, residual risk level, and supervision plan.
13.Risk Assessment Review: Should be conducted on a regular basis. Reviewers should have sufficient oversight of the mission or activity and controls to provide valid input on changes or adjustments needed. If the residual risk rises above the level already approved, operations should cease until the appropriate approval authority is contacted and approves continued operations.
14.Feedback and Lessons Learned: Provide specific input on the effectiveness of risk controls and their contribution to mission success or failure. Include recommendations for new or revised controls, practicable solutions, or alternate actions. Submit and brief valid lessons learned as necessary to persons affected.
15.Additional Comments or Remarks: Preparer or approval authority provides any additional comments, remarks, or information to support the integration of risk management.
Additional Guidance: Blocks
DD FORM 2977, SEP 2014 |
Page 3 of 3 |
Other PDF Templates
Trust Restatement Form - It is recommended to keep a copy of the amendment for personal records.
The WC-200A Georgia form is a crucial document used to request a change of physician or additional treatment in workers' compensation cases. Properly filling out this form is essential for ensuring that employees receive the medical care they need while also complying with state regulations. For more information and to access the form, visit https://georgiapdf.com. Take action now to ensure your rights are protected by filling out the form below.
Dd Form 2870 Download - This form supports the documentation of ongoing dental care requirements.
Documents used along the form
The DD Form 2977, or Deliberate Risk Assessment Worksheet, is an essential document used to evaluate risks associated with military missions and tasks. To ensure a comprehensive risk management process, several other forms and documents are often utilized alongside it. Below are four commonly used documents that complement the DD Form 2977.
- DD Form 4145: This form, known as the Risk Management Plan, outlines the overall strategy for managing risks associated with a specific mission or operation. It details the objectives, risk levels, and the measures that will be taken to mitigate those risks.
- OPORD (Operation Order): An OPORD provides detailed instructions for conducting military operations. It includes the mission's purpose, execution, and the logistics necessary to ensure the mission's success. Risk assessments are often incorporated within the OPORD to address potential hazards.
- Non-disclosure Agreement: To protect sensitive information in business transactions, refer to the essential Non-disclosure Agreement guidelines for ensuring confidentiality and compliance.
- DA Form 7566: This form is used for the Army's Composite Risk Management process. It serves to identify and assess risks, implement controls, and evaluate the effectiveness of those controls. It complements the DD Form 2977 by providing a structured approach to risk management.
- AF Form 102: The Air Force uses this form for its Risk Management process. It helps to document and analyze potential risks associated with Air Force missions, ensuring that proper measures are in place to mitigate those risks.
Utilizing these documents in conjunction with the DD Form 2977 enhances the effectiveness of risk management efforts. Together, they provide a robust framework for identifying, assessing, and controlling risks, ultimately contributing to mission success and safety.
Similar forms
The DD Form 214, Certificate of Release or Discharge from Active Duty, serves a different purpose but shares a similar goal of documenting military service. Like the DD 2977, it is a critical form used by service members. The DD 214 provides a summary of a service member's time in the military, including the nature of their discharge. Both forms require detailed information and signatures from authorized personnel to ensure accuracy and accountability.
The DD Form 1380, Record of Individual Performance of Duty, is another document that aligns with the DD 2977 in terms of assessing performance and risk. This form records individual performance during a specific duty assignment. Just as the DD 2977 evaluates risks associated with a mission, the DD 1380 evaluates the effectiveness and outcomes of an individual's actions in a given role. Both forms require input from supervisors and are essential for maintaining operational standards.
For those involved in the sale or purchase of a recreational vehicle in Texas, understanding the required documentation is crucial. The Texas RV Bill of Sale form is essential for facilitating this process, and it ensures that every detail of the transaction is recorded properly. This form serves not only to protect both parties in the exchange but is also necessary for registration and tax purposes, making it a pivotal part of the transaction. For more detailed guidance, you can refer to autobillofsaleform.com/rv-bill-of-sale-form/texas-rv-bill-of-sale-form/.
The DA Form 1059, Academic Evaluation Report, provides a record of a soldier's academic performance. Similar to the DD 2977, it assesses the effectiveness of training and identifies areas for improvement. Both documents aim to enhance performance and ensure that individuals are prepared for their responsibilities. They require evaluations from authorized personnel to validate the findings and recommendations included.
The AF Form 475, Education/Training Report, is used in the Air Force to evaluate training and performance. Like the DD 2977, it focuses on assessing risks and outcomes related to specific tasks. Both forms include sections for feedback and recommendations, aiming to improve future performance and mitigate risks associated with training and operations.
The DD Form 2792, Family Member Medical Summary, documents medical information for military families. While it may seem unrelated, it shares a common thread with the DD 2977 in that both forms require careful consideration of risks. The DD 2792 assesses health risks that could impact a service member's mission readiness, similar to how the DD 2977 evaluates operational risks.
The DA Form 638, Recommendation for Award, is another document that recognizes individual contributions. It parallels the DD 2977 in that both require detailed descriptions of actions and outcomes. While the DD 638 focuses on achievements, the DD 2977 focuses on risk assessment. Both forms are essential for maintaining accountability and recognizing the efforts of service members.
The SF 86, Questionnaire for National Security Positions, is used for background checks. It assesses risks related to security clearances. Similar to the DD 2977, it requires comprehensive information to evaluate potential risks. Both forms are critical for ensuring the safety and security of military operations and personnel.
The DD Form 2992, Medical Recommendation for Flying or Special Operational Duty, evaluates medical fitness for specific duties. It shares similarities with the DD 2977 in that both assess risks that could affect operational capabilities. Each form requires input from qualified personnel to determine the best course of action regarding an individual's fitness for duty.
The DA Form 4187, Personnel Action, documents changes in a service member's status. While it focuses on personnel management, it is similar to the DD 2977 in that it requires clear documentation of actions and decisions. Both forms play a role in maintaining the integrity and readiness of military operations.
Finally, the DD Form 1610, Request and Authorization for TDY Travel of DOD Personnel, outlines travel for duty assignments. It parallels the DD 2977 by assessing risks associated with travel and operational readiness. Both forms require careful planning and approval from authorized personnel to ensure that missions are conducted safely and effectively.
Dos and Don'ts
Do's
- Provide accurate and complete information in all sections of the form.
- Use clear and concise language when describing the mission or task.
- Review the risk assessment matrix carefully to determine the correct risk levels.
- Ensure that all necessary signatures are obtained before submitting the form.
Don'ts
- Do not leave any sections blank; incomplete forms may delay processing.
- Avoid using vague terms or jargon that could lead to misunderstandings.
- Do not underestimate hazards; take them seriously to ensure safety.
- Refrain from submitting the form without a thorough review of all details.
Key takeaways
When filling out the DD Form 2977, also known as the Deliberate Risk Assessment Worksheet, there are several important points to keep in mind:
- Mission/Task Description: Clearly describe the mission or task for which the risk assessment is being conducted. This provides context for the assessment.
- Date: Enter the date in the specified format (YYYYMMDD). This helps track when the assessment was completed.
- Prepared By: Include the name, rank, duty title, unit, work email, and telephone number of the individual conducting the assessment. This ensures accountability and allows for follow-up if necessary.
- Hazard Identification: Specify hazards associated with each subtask. Identifying hazards is crucial for assessing risk effectively.
- Initial Risk Level: Use the risk assessment matrix to determine the initial risk level based on the probability and severity of each hazard. This step is essential for understanding the potential impact of risks.
- Control Measures: List the risk mitigation resources and controls that can reduce the identified risks. This section is vital for planning how to manage risks effectively.
- Approval Process: The mission or task must be approved or disapproved based on the overall risk assessment. This includes evaluating the controls, residual risk level, and supervision plan.
By following these key takeaways, individuals can ensure a thorough and effective risk assessment process using the DD Form 2977.
How to Use Dd 2977
Once you have gathered all the necessary information, you are ready to fill out the DD Form 2977. This process involves several steps that will ensure you complete the form accurately and effectively. Please follow the instructions below carefully to avoid any delays in processing.
- Mission/Task Description: Provide a brief overview of the mission or task for which the risk assessment is being conducted.
- Date: Enter the date in the format YYYYMMDD.
- Prepared By: Fill in the details of the individual conducting the assessment, including:
- Name (Last, First Middle Initial)
- Rank/Grade
- Duty Title/Position
- Unit
- Work Email
- Telephone (DSN/Commercial, including area code)
- UIC/CIN (as required)
- Training Support/Lesson Plan or OPORD (as required)
- Signature of Preparer
- Subtask/Substep of Mission/Task: Describe any subtasks or substeps that require risk management.
- Hazard: Identify the specific hazards related to the subtask mentioned in the previous step.
- Initial Risk Level: Assess the probability and severity of each hazard using the risk assessment matrix and document the risk level.
- Control: List the risk mitigation measures or controls that will help reduce the identified risks.
- How to Implement / Who Will Implement: Describe how each control will be executed and identify the responsible individual or unit.
- Residual Risk Level: After implementing controls, evaluate the resulting risk level based on probability and severity.
- Overall Residual Risk Level: Assign a final risk level that reflects the highest residual risk after controls have been put in place.
- Supervision Plan and Recommended Course of Action: Outline specific supervisory tasks and responsibilities, along with a recommended course of action based on the risk assessment.
- Approval or Disapproval of Mission or Task: The approval authority will provide their name, rank, duty title, and signature to indicate approval or disapproval.
- Risk Assessment Review: Document the date, reviewer’s last name, rank, duty title, and signature for ongoing operations.
- Feedback and Lessons Learned: Include any insights regarding the effectiveness of risk controls and suggestions for improvement.
- Additional Comments or Remarks: Add any extra comments or information that may assist in risk management.