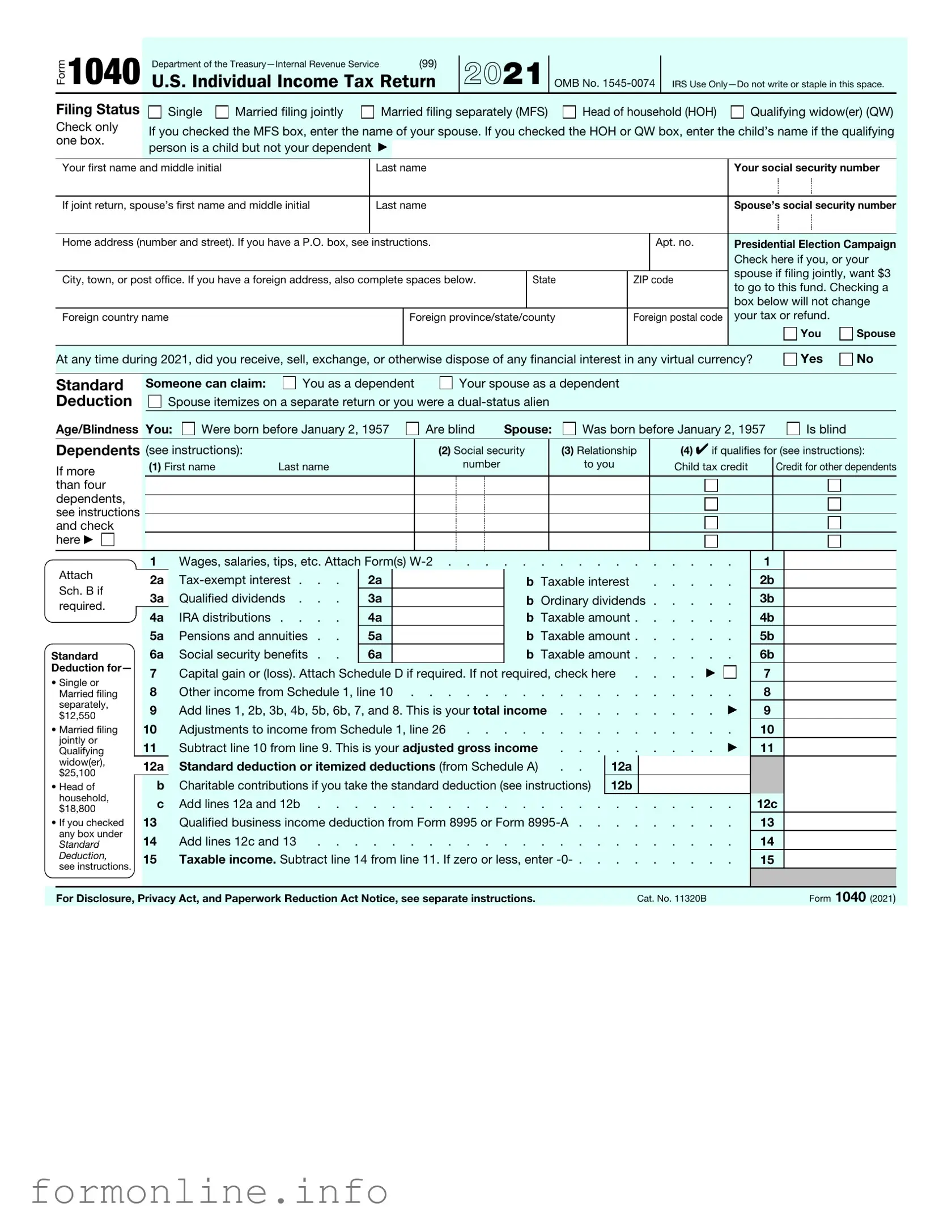
Fill Out a Valid IRS 1040 Form
The IRS 1040 form is a crucial document for individuals in the United States when it comes to filing annual income taxes. This form allows taxpayers to report their income, claim deductions, and calculate their tax liability. It serves as the foundation for various tax situations, accommodating everything from simple wage earners to those with complex financial scenarios, including self-employment income and investment earnings. Taxpayers can also utilize schedules attached to the 1040 form to provide additional details about specific income types or deductions. Understanding the different sections of the form is essential, as it includes personal information, filing status, and various credits that can reduce tax owed. Whether you’re filing for the first time or have years of experience, navigating the 1040 form can significantly impact your tax return and potential refund.
Common mistakes
When filling out the IRS 1040 form, individuals often encounter several pitfalls that can lead to errors or delays in processing. Below is a list of common mistakes to avoid:
-
Incorrect Personal Information:
Many taxpayers forget to double-check their name, Social Security number, and address. Even a small typo can cause significant issues.
-
Filing Status Errors:
Selecting the wrong filing status can lead to incorrect tax calculations. Understanding whether to file as single, married filing jointly, or head of household is crucial.
-
Math Mistakes:
Simple addition or subtraction errors can change your tax liability. Always review calculations carefully or consider using tax software to minimize errors.
-
Missing Signatures:
Submitting the form without a signature is a common oversight. Remember, both spouses must sign if filing jointly.
-
Omitting Income:
Some individuals forget to report all sources of income, such as freelance work or interest from savings accounts. This can result in penalties.
-
Ignoring Deductions and Credits:
Many taxpayers overlook available deductions and credits. Researching these can lead to significant savings.
-
Improperly Reporting Dependents:
Claiming dependents incorrectly can lead to complications. Ensure that the dependent meets IRS requirements.
-
Not Using the Correct Form:
Choosing the wrong version of the 1040 form can cause delays. Be sure to use the form that corresponds to your tax situation.
-
Failing to Keep Copies:
Many forget to keep a copy of their completed tax return. Retaining this documentation is important for future reference and audits.
By being mindful of these common mistakes, individuals can ensure a smoother filing process and avoid unnecessary complications with the IRS.
Preview - IRS 1040 Form
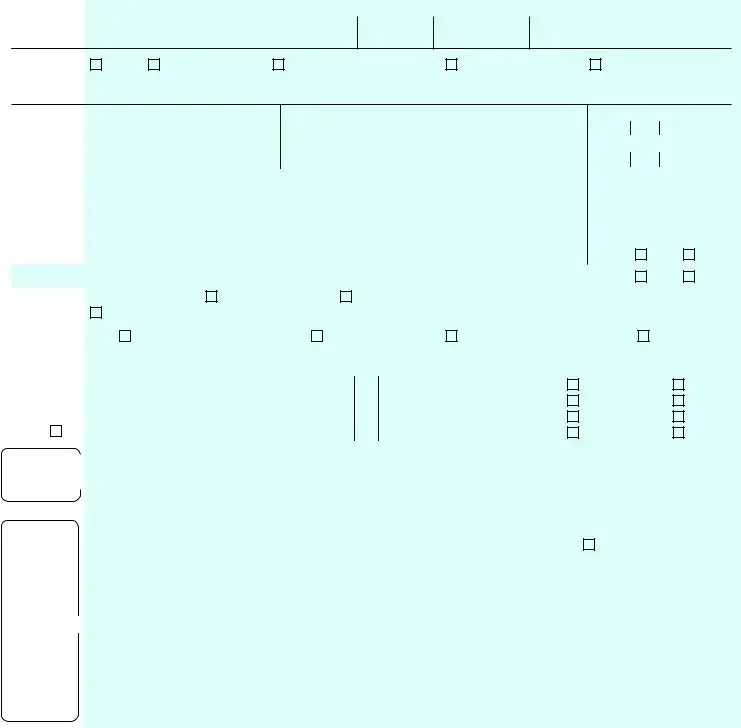
Form
1040
Department of the |
(99) |
U.S. Individual Income Tax Return
2021
OMB No.
IRS Use
Filing Status
Check only one box.
|
Single |
|
Married filing jointly |
|
Married filing separately (MFS) |
|
Head of household (HOH) |
|
Qualifying widow(er) (QW) |
|
|
|
|
|
If you checked the MFS box, enter the name of your spouse. If you checked the HOH or QW box, enter the child’s name if the qualifying person is a child but not your dependent ▶ 
|
Your first name and middle initial |
|
|
|
|
Last name |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Your social security number |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
If joint return, spouse’s first name and middle initial |
Last name |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Spouse’s social security number |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
Home address (number and street). If you have a P.O. box, see instructions. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Apt. no. |
Presidential Election Campaign |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Check here if you, or your |
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
spouse if filing jointly, want $3 |
||||||||||||||
|
City, town, or post office. If you have a foreign address, also complete spaces below. |
|
State |
|
|
|
|
ZIP code |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
to go to this fund. Checking a |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
box below will not change |
||||||||||||||
|
Foreign country name |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Foreign province/state/county |
|
|
|
|
Foreign postal code |
your tax or refund. |
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
You |
|
|
Spouse |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
At any time during 2021, did you receive, sell, exchange, or otherwise dispose of any financial interest in any virtual currency? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Yes |
|
|
No |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Standard |
|
Someone can claim: |
|
|
|
You as a dependent |
|
|
Your spouse as a dependent |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Deduction |
|
|
|
|
|
Spouse itemizes on a separate return or you were a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Age/Blindness You: |
|
|
Were born before January 2, 1957 |
|
|
Are blind |
Spouse: |
|
|
Was born before January 2, 1957 |
|
|
|
|
Is blind |
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Dependents (see instructions): |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(2) Social security |
|
(3) Relationship |
(4) ✔ if qualifies for (see instructions): |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
If more |
|
|
(1) First name |
Last name |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
number |
|
|
|
|
|
to you |
Child tax credit |
|
|
Credit for other dependents |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
than four |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
dependents, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
see instructions |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
and check |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
here ▶ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Attach |
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
Wages, salaries, tips, etc. Attach Form(s) |
. |
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
a |
|
|
2a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
b Taxable interest |
. . . . |
|
|
. |
|
|
2b |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
Sch. B if |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
3 |
a |
|
|
Qualified dividends . . . |
3a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
b Ordinary dividends . . . . |
. |
|
|
3b |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
required. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
4a |
IRA distributions . . . . |
4a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
b Taxable amount |
. |
|
|
4b |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5a |
Pensions and annuities . . |
5a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
b Taxable amount |
. |
|
|
5b |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
Standard |
|
|
6a |
Social security benefits . . |
6a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
b Taxable amount |
. |
|
|
6b |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Deduction for— |
7 |
|
|
|
|
Capital gain or (loss). Attach Schedule D if required. If not required, check here . |
. . . ▶ |
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
• Single or |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
8 |
|
|
|
|
Other income from Schedule 1, line 10 |
. |
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Married filing |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
separately, |
9 |
|
|
|
|
Add lines 1, 2b, 3b, 4b, 5b, 6b, 7, and 8. This is your total income |
▶ |
|
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
$12,550 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
• Married filing |
10 |
|
|
|
|
Adjustments to income from Schedule 1, line 26 |
. |
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
jointly or |
11 |
|
|
|
|
Subtract line 10 from line 9. This is your adjusted gross income |
. . . . . . . . . |
|
|
▶ |
|
11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Qualifying |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
widow(er), |
|
|
|
12 |
a |
|
|
Standard deduction or itemized deductions (from Schedule A) |
. . |
12a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
$25,100 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
b |
Charitable contributions if you take the standard deduction (see instructions) |
12b |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
• Head of |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
household, |
|
|
|
c |
Add lines 12a and 12b |
. |
|
|
12c |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
$18,800 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
• If you checked |
13 |
|
|
|
|
Qualified business income deduction from Form 8995 or Form |
. |
|
|
13 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
any box under |
14 |
|
|
|
|
Add lines 12c and 13 |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
|
|
. |
|
|
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Standard |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Deduction, |
15 |
|
|
|
|
Taxable income. Subtract line 14 from line 11. If zero or less, enter |
. |
|
|
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
see instructions. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
For Disclosure, Privacy Act, and Paperwork Reduction Act Notice, see separate instructions. |
|
|
|
|
Cat. No. 11320B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Form 1040 (2021) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
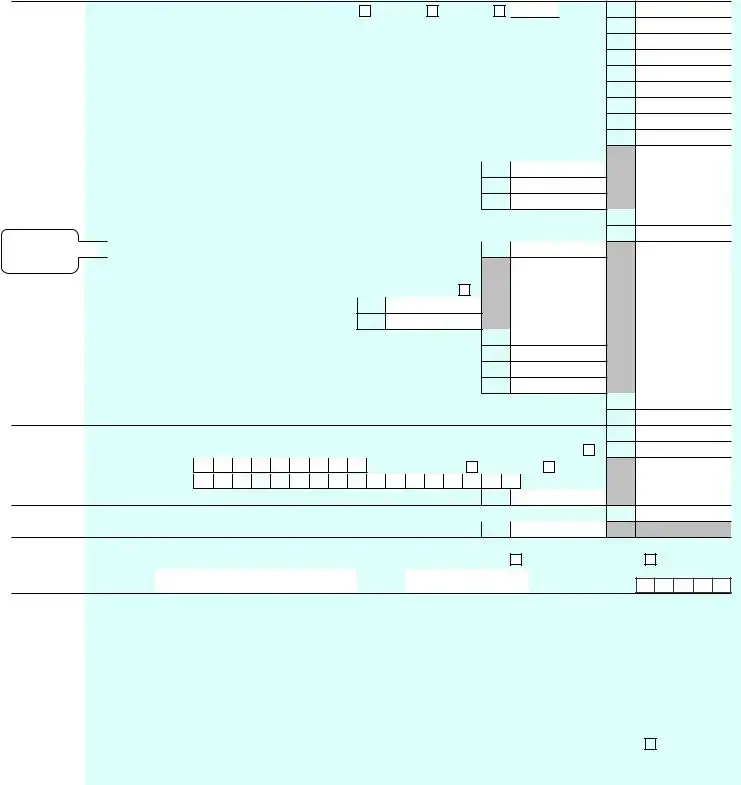
|
|
Form 1040 (2021) |
Page 2 |
|
16 |
Tax (see instructions). Check if any from Form(s): 1 |
8814 |
2 |
4972 |
|
3 |
|
|
. . |
16 |
|
|||
|
17 |
Amount from Schedule 2, line 3 |
. . . . . . . . |
17 |
|
||||||||||
|
18 |
Add lines 16 and 17 |
. . . . . . . . |
18 |
|
||||||||||
|
19 |
Nonrefundable child tax credit or credit for other dependents from Schedule 8812 |
19 |
|
|||||||||||
|
20 |
Amount from Schedule 3, line 8 |
. . . . . . . . |
20 |
|
||||||||||
|
21 |
Add lines 19 and 20 |
. . . . . . . . |
21 |
|
||||||||||
|
22 |
Subtract line 21 from line 18. If zero or less, enter |
. . . . . . . . |
22 |
|
||||||||||
|
23 |
Other taxes, including |
. . . . . . . . |
23 |
|
||||||||||
|
24 |
Add lines 22 and 23. This is your total tax |
. . . . . |
. . |
▶ |
24 |
|
||||||||
|
25 |
Federal income tax withheld from: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
a |
Form(s) |
|
25a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
b |
Form(s) 1099 |
|
25b |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
c |
Other forms (see instructions) |
|
25c |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
d |
Add lines 25a through 25c |
. . . . . . . . |
25d |
|
||||||||||
If you have a |
26 |
2021 estimated tax payments and amount applied from 2020 return . . |
. . . . . . . . |
26 |
|
||||||||||
27a |
Earned income credit (EIC) |
|
27a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
qualifying child, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
attach Sch. EIC. |
|
Check here if you were born after January 1, 1998, and before |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
January 2, 2004, and you satisfy all the other requirements for |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
taxpayers who are at least age 18, to claim the EIC. See instructions ▶ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
b |
Nontaxable combat pay election . . . . |
27b |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
c |
Prior year (2019) earned income . . . . |
27c |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
28 |
Refundable child tax credit or additional child tax credit from Schedule 8812 |
|
28 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
29 |
American opportunity credit from Form 8863, line 8 |
|
29 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
30 |
Recovery rebate credit. See instructions |
|
30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
31 |
Amount from Schedule 3, line 15 |
|
31 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
32 |
Add lines 27a and 28 through 31. These are your total other payments and refundable credits |
▶ |
32 |
|
||||||||||
|
33 |
Add lines 25d, 26, and 32. These are your total payments . . . . |
. . . . . |
. . |
▶ |
33 |
|
||||||||
Refund |
34 |
If line 33 is more than line 24, subtract line 24 from line 33. This is the amount you overpaid |
|
. . |
34 |
|
|||||||||
35a |
Amount of line 34 you want refunded to you. If Form 8888 is attached, check here . . |
. |
▶ |
|
35a |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
Direct deposit? |
▶ b |
Routing number |
|
▶ c Type: |
|
|
Checking |
|
Savings |
|
|
||||
See instructions. |
▶ d |
Account number |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
36 |
Amount of line 34 you want applied to your 2022 estimated tax . |
. |
▶ |
|
36 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Amount |
37 |
Amount you owe. Subtract line 33 from line 24. For details on how to pay, see instructions |
|
. |
▶ |
37 |
|
||||||||
You Owe |
38 |
Estimated tax penalty (see instructions) . . . |
. . . . . |
. |
▶ |
|
38 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Third Party |
Do |
you want to allow another person to discuss this return with the IRS? See |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Designee |
instructions |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. |
▶ |
Yes. Complete below. |
No |
|||||||||
|
Designee’s |
|
Phone |
|
|
|
|
|
Personal identification |
|
|||||
|
name ▶ |
|
no. ▶ |
|
|
|
|
|
number (PIN) ▶ |
|
|
||||
Sign
Here
Joint return? See instructions. Keep a copy for your records.
Under penalties of perjury, I declare that I have examined this return and accompanying schedules and statements, and to the best of my knowledge and belief, they are true, correct, and complete. Declaration of preparer (other than taxpayer) is based on all information of which preparer has any knowledge.
Your signature |
Date |
Your occupation |
If the IRS sent you an Identity |
||||||
|
|
|
Protection PIN, enter it here |
||||||
|
|
|
(see inst.) ▶ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Spouse’s signature. If a joint return, both must sign. |
Date |
Spouse’s occupation |
If the IRS sent your spouse an |
||||||
▲ |
|
|
Identity Protection PIN, enter it here |
||||||
|
|
|
(see inst.) ▶ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Phone no. |
Email address |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Paid |
Preparer’s name |
Preparer’s signature |
Date |
PTIN |
|
Check if: |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Preparer |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Firm’s name ▶ |
|
|
|
Phone no. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Use Only |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Firm’s address ▶ |
|
|
|
Firm’s EIN |
▶ |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
Go to www.irs.gov/Form1040 for instructions and the latest information. |
|
|
|
|
|
Form 1040 (2021) |
|||||
Other PDF Templates
Imm 5645 - The IMM 5645 form gathers comprehensive family information for Canadian immigration applications.
The detailed Trailer Bill of Sale example serves as a vital resource for anyone looking to formalize the transfer of trailer ownership in Florida, ensuring that all necessary information is captured to facilitate a legal transaction.
Llc Membership Certificate Template - Each section of this form serves a specific purpose.
Documents used along the form
When filing your taxes, the IRS 1040 form is the primary document used to report your income and calculate your tax liability. However, several other forms and documents are often required to provide additional information or support your tax return. Below is a list of common forms and documents that may accompany the 1040 form.
- W-2 Form: This form is issued by your employer and reports your annual wages and the taxes withheld from your paycheck. It is essential for accurately calculating your taxable income.
- 1099 Forms: These forms report various types of income you may receive outside of regular employment, such as freelance earnings, interest, dividends, or retirement distributions.
- New York ATV Bill of Sale Form: For individuals transferring ownership of all-terrain vehicles, consult the essential New York ATV Bill of Sale documentation to ensure a smooth and legal transaction.
- Schedule A: If you choose to itemize your deductions instead of taking the standard deduction, this form is used to list eligible expenses like mortgage interest, medical expenses, and charitable contributions.
- Schedule C: For self-employed individuals, this form is used to report income and expenses related to a business. It helps determine your net profit or loss.
- Schedule D: This form is for reporting capital gains and losses from the sale of assets, such as stocks or real estate. It helps calculate any taxes owed on these transactions.
- Form 8889: If you have a Health Savings Account (HSA), this form is used to report contributions and distributions, ensuring that you comply with tax regulations.
- Form 8862: This form is required if you are claiming the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) after it was previously disallowed. It helps the IRS verify your eligibility.
- Form 1040-SR: Designed for seniors, this form is similar to the 1040 but features larger print and a simplified layout. It can be used by taxpayers aged 65 and older.
- Form 4506-T: This form allows you to request a transcript of your tax return from the IRS. It's useful if you need to verify income for loans or other purposes.
Each of these forms and documents plays a crucial role in ensuring your tax return is complete and accurate. Depending on your financial situation, you may need one or several of these forms to support your 1040 filing. Being organized and thorough can help you avoid delays and potential issues with your tax return.
Similar forms
The IRS 1040 form is often compared to the W-2 form, which employers provide to their employees. The W-2 summarizes an employee's earnings and the taxes withheld throughout the year. Like the 1040, the W-2 is crucial for accurate tax reporting. While the 1040 is used by individuals to report their total income and calculate their tax obligations, the W-2 serves as a foundational document that informs the 1040, detailing how much income was earned and what taxes have already been paid. Both documents are essential for ensuring compliance with tax laws.
The process of transferring ownership of a mobile home can often involve a range of legal documents, notably the Mobile Home Bill of Sale, which plays a critical role in ensuring that all details of the transaction are formally recorded. This document serves as proof of the sale, protecting both the buyer and the seller from potential disputes, and is vital for a seamless transfer of property rights.
Another document similar to the 1040 is the 1099 form, which is used for reporting income received from sources other than traditional employment. Freelancers, independent contractors, and self-employed individuals often receive 1099 forms. Like the 1040, the 1099 provides a detailed account of income earned, and this information must be reported on the 1040. The 1099 serves as a reminder that not all income comes from a W-2 job, and it highlights the importance of reporting diverse income sources accurately.
The Schedule C form is another document that bears resemblance to the 1040. This form is used by self-employed individuals to report income and expenses related to their business. Just as the 1040 captures an individual's overall financial picture, the Schedule C provides a more detailed view of business operations. The information from the Schedule C feeds into the 1040, affecting the overall tax liability. Both forms work together to ensure that self-employed individuals report their earnings accurately and pay the appropriate amount of taxes.
The Schedule A form is also similar to the 1040 in that it allows taxpayers to itemize deductions instead of taking the standard deduction. This form provides a detailed breakdown of eligible expenses, such as medical costs, mortgage interest, and charitable contributions. By itemizing on Schedule A, taxpayers can potentially lower their taxable income, much like how various credits and deductions on the 1040 can reduce tax liability. Both forms require careful documentation and consideration to maximize tax benefits.
The Form 8889, which is used for Health Savings Accounts (HSAs), shares similarities with the 1040 as well. This form reports contributions to and distributions from HSAs. Like the 1040, the 8889 plays a critical role in ensuring that taxpayers accurately report their financial activities related to healthcare savings. Contributions to an HSA can be tax-deductible, and distributions used for qualified medical expenses are tax-free. Thus, the 8889 complements the 1040 by providing additional details that can affect overall tax calculations.
The Form 8862, which is used to claim the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) after a disallowance, is another document that connects to the 1040. This form requires individuals to provide specific information to qualify for the EITC again. Similar to the 1040, it emphasizes the importance of meeting eligibility criteria and provides a pathway for taxpayers to recover benefits they may have lost. Both forms work in tandem to ensure that taxpayers receive the credits and deductions they are entitled to, promoting fairness in the tax system.
Finally, the Form 1040-X, the amended tax return, is closely related to the original 1040. This form is used to make corrections or updates to a previously filed 1040. Life circumstances can change, and taxpayers may discover new information that impacts their tax situation. The 1040-X allows individuals to adjust their income, deductions, or credits. Both forms reflect the ongoing nature of tax compliance, highlighting that tax reporting is not always a one-time event but may require updates and revisions as new information becomes available.
Dos and Don'ts
When filling out the IRS 1040 form, it is important to follow certain guidelines to ensure accuracy and compliance. Here are some things you should and shouldn't do:
- Do read the instructions carefully before starting.
- Do double-check all personal information for accuracy.
- Do report all sources of income, including wages, interest, and dividends.
- Do take advantage of deductions and credits you qualify for.
- Do sign and date the form before submitting it.
- Don't leave any required fields blank.
- Don't forget to include your Social Security number.
- Don't submit the form without reviewing it for errors.
- Don't ignore deadlines for filing and payment.
- Don't forget to keep a copy of your completed form for your records.
Key takeaways
Filling out the IRS 1040 form can seem daunting, but understanding a few key points can simplify the process. Here are some essential takeaways to keep in mind:
- Accuracy is crucial. Ensure all information is correct to avoid delays in processing your return.
- Know your deductions. Familiarize yourself with available deductions and credits that may lower your tax liability.
- Use the right filing status. Selecting the appropriate filing status can significantly impact your tax rate and eligibility for certain deductions.
- Keep records. Maintain copies of your completed forms and supporting documents for future reference and potential audits.
Being informed about these aspects can lead to a smoother tax filing experience. Take your time and don’t hesitate to seek assistance if needed.
How to Use IRS 1040
Filling out the IRS 1040 form is an essential step in preparing your annual tax return. Once completed, you will need to submit it to the IRS, ensuring that you meet all deadlines to avoid penalties. Here’s how to fill out the form step by step.
- Gather all necessary documents, including W-2s, 1099s, and any other income statements.
- Begin with your personal information. Enter your name, address, and Social Security number at the top of the form.
- Indicate your filing status. Choose from options like single, married filing jointly, married filing separately, head of household, or qualifying widow(er).
- Report your income. Fill in the total income from all sources on the designated lines.
- Adjust your income if necessary. Use the adjustments section to account for contributions to retirement accounts or student loan interest.
- Calculate your adjusted gross income (AGI). This figure is found by subtracting adjustments from your total income.
- Claim deductions. Decide whether to take the standard deduction or itemize your deductions. Fill in the appropriate amounts.
- Determine your taxable income. Subtract your deductions from your AGI.
- Calculate your tax liability using the tax tables provided in the instructions.
- Account for any tax credits. List any applicable credits that reduce your tax liability.
- Calculate your total tax owed or refund due. Compare your total tax liability with the amount you’ve already paid through withholding or estimated payments.
- Sign and date the form. If filing jointly, both spouses must sign.
- Submit your completed form. You can file electronically or mail it to the appropriate IRS address.