Fill Out a Valid IRS 8300 Form
The IRS 8300 form plays a crucial role in maintaining transparency in financial transactions, particularly those involving cash payments exceeding $10,000. This form is primarily used by businesses and individuals to report large cash transactions to the Internal Revenue Service. By doing so, it helps to combat money laundering and other financial crimes. When a business receives cash payments that meet or exceed this threshold, they are required to file the form within 15 days of the transaction. The information collected includes details about the payer, the amount received, and the nature of the transaction. Additionally, the IRS 8300 form must be filed even if the cash payment is part of a series of smaller transactions that cumulatively exceed the reporting limit. Understanding the requirements and implications of this form is essential for compliance, as failure to report can lead to significant penalties. Businesses must also be aware of their responsibilities regarding customer privacy and data protection when handling such sensitive information.
Common mistakes
-
Failing to provide complete information about the transaction. It is essential to include all required details to avoid delays.
-
Not identifying the person or business making the cash payment correctly. Ensure names and addresses are accurate.
-
Omitting the date of the transaction. This information is crucial for record-keeping and compliance.
-
Incorrectly reporting the amount of cash received. Double-check calculations to ensure accuracy.
-
Neglecting to sign and date the form. A signature is required to validate the submission.
-
Using outdated versions of the form. Always download the latest version from the IRS website to ensure compliance.
-
Not keeping a copy of the completed form for personal records. Retaining a copy can be beneficial for future reference.
-
Failing to submit the form within the required timeframe. Timeliness is important to avoid penalties.
-
Providing inaccurate identification numbers. Ensure that Social Security numbers or Employer Identification Numbers are correct.
-
Forgetting to report multiple transactions. If there are several cash payments, each must be reported separately.
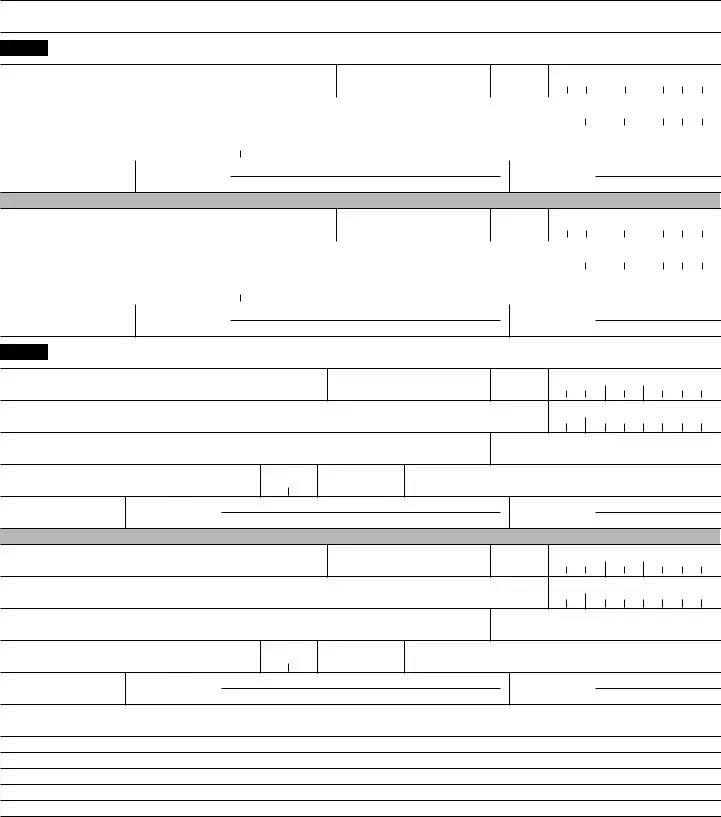
Preview - IRS 8300 Form

IRSForm 8300
(Rev. August 2014)
Department of the Treasury Internal Revenue Service
Report of Cash Payments Over $10,000
Received in a Trade or Business
See instructions for definition of cash.
Use this form for transactions occurring after August 29, 2014. Do not use prior versions after this date.
For Privacy Act and Paperwork Reduction Act Notice, see the last page.
FinCENForm 8300
(Rev. August 2014) OMB No.
Department of the Treasury
Financial Crimes
Enforcement Network
1 |
Check appropriate box(es) if: |
a |
Amends prior report; |
b |
Suspicious transaction.
Part I |
|
Identity of Individual From Whom the Cash Was Received |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
2 |
If more than one individual is involved, check here and see instructions |
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
3 |
Last name |
|
4 First name |
|
|
5 M.I. |
6 Taxpayer identification number |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
Address (number, street, and apt. or suite no.) |
|
|
|
8 Date of |
birth . . . |
|
|
M M D D Y Y Y Y |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(see instructions) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
9 |
City |
|
10 State |
11 ZIP code |
12 |
Country (if not U.S.) |
|
13 Occupation, profession, or business |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14Identifying document (ID)
aDescribe ID c Number
b Issued by
Part II Person on Whose Behalf This Transaction Was Conducted
15 If this transaction was conducted on behalf of more than one person, check here and see instructions . . . . . . . . . . .
16Individual’s last name or organization’s name
17First name
18M.I.
19Taxpayer identification number
20Doing business as (DBA) name (see instructions)
Employer identification number
21Address (number, street, and apt. or suite no.)
22Occupation, profession, or business
23City
24State
25ZIP code
26Country (if not U.S.)
27Alien identification (ID)
aDescribe ID c Number
b Issued by
Part III Description of Transaction and Method of Payment
28Date cash received
M M D D Y Y Y Y
29Total cash received
$.00
30
If cash was received in more than one payment, check here . . .
31Total price if different from item 29
$.00
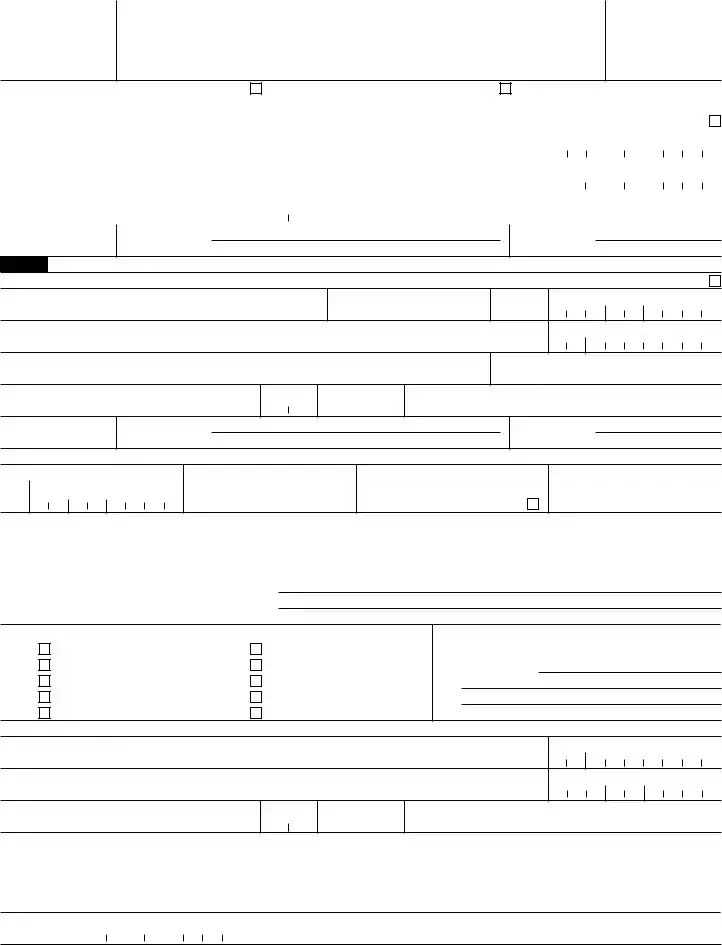
32Amount of cash received (in U.S. dollar equivalent) (must equal item 29) (see instructions):
a |
U.S. currency |
$ |
.00 |
(Amount in $100 bills or higher $ |
.00 ) |
|||||
b |
Foreign currency |
$ |
.00 |
(Country |
|
) |
|
|||
c |
|
$ |
|
} |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cashier’s check(s) |
.00 |
Issuer’s name(s) and serial number(s) of the monetary instrument(s) |
||||||||
|
||||||||||
d |
Money order(s) |
$ |
.00 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
e |
Bank draft(s) |
$ |
.00 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
f |
Traveler’s check(s) |
$ |
.00 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
33Type of transaction
a |
Personal property purchased |
f |
b |
Real property purchased |
g |
c |
Personal services provided |
h |
d |
Business services provided |
i |
e |
Intangible property purchased |
j |
Debt obligations paid Exchange of cash Escrow or trust funds
Bail received by court clerks Other (specify in item 34)
34Specific description of property or service shown in
33.Give serial or registration number, address, docket number, etc.
Part IV Business That Received Cash
35Name of business that received cash
36Employer identification number
37Address (number, street, and apt. or suite no.)
Social security number
38City
39State
40ZIP code
41Nature of your business
42Under penalties of perjury, I declare that to the best of my knowledge the information I have furnished above is true, correct, and complete.
Signature
43Date of signature
|
|
|
|
|
|
Title |
|
|
|
F |
Authorized official |
F |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|||||||
|
M M |
D D |
Y Y Y Y |
44 Type or print name of contact person |
|
45 Contact telephone number |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IRS Form 8300 (Rev. |
Cat. No. 62133S |
FinCEN Form 8300 (Rev. |
IRS Form 8300 (Rev.
Multiple Parties
(Complete applicable parts below if box 2 or 15 on page 1 is checked.)
Part I
3Last name
4First name
5M.I.
6Taxpayer identification number
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
Address (number, street, and apt. or suite no.) |
|
8 Date of birth . . . |
M M D D Y Y Y Y |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
(see instructions) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
City |
10 State |
11 ZIP code |
12 Country (if |
not U.S.) |
13 Occupation, profession, or business |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14Identifying document (ID)
aDescribe ID c Number
b Issued by
3Last name
4First name
5M.I.
6Taxpayer identification number
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
Address (number, street, and apt. or suite no.) |
|
8 Date of birth . . . |
M M D D Y Y Y Y |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
(see instructions) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
9 |
City |
10 State |
11 ZIP code |
12 Country (if |
not U.S.) |
13 Occupation, profession, or business |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
14Identifying document (ID)
aDescribe ID c Number
b Issued by
Part II
16Individual’s last name or organization’s name
17First name
18M.I.
19Taxpayer identification number
20Doing business as (DBA) name (see instructions)
Employer identification number
21Address (number, street, and apt. or suite no.)
22Occupation, profession, or business
23City
24State
25ZIP code
26Country (if not U.S.)
27Alien identification (ID)
aDescribe ID c Number
b Issued by
16Individual’s last name or organization’s name
17First name
18M.I.
19Taxpayer identification number
20Doing business as (DBA) name (see instructions)
Employer identification number
21Address (number, street, and apt. or suite no.)
22Occupation, profession, or business
23City
24State
25ZIP code
26Country (if not U.S.)
27Alien identification (ID)
aDescribe ID c Number
b Issued by
Comments – Please use the lines provided below to comment on or clarify any information you entered on any line in Parts I, II, III, and IV
IRS Form 8300 (Rev. |
FinCEN Form 8300 (Rev. |
IRS Form 8300 (Rev. |
Page 3 |
FinCEN Form 8300 (Rev. |
Section references are to the Internal Revenue Code unless otherwise noted.
Future Developments
For the latest information about developments related to Form 8300 and its instructions, such as legislation enacted after they were published, go to www.irs.gov/form8300.
Important Reminders
•Section 6050I (26 United States Code (U.S.C.) 6050I) and 31 U.S.C. 5331 require that certain information be reported to the IRS and the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN). This information must be reported on IRS/FinCEN Form 8300.
•Item 33, box i, is to be checked only by clerks of the court; box d is to be checked by bail bondsmen. See Item 33 under Part III, later.
•The meaning of the word “currency” for purposes of 31 U.S.C. 5331 is the same as for the word “cash” (See Cash under Definitions, later).
General Instructions
Who must file. Each person engaged in a trade or business who, in the course of that trade or business, receives more than $10,000 in cash in one transaction or in two or more related transactions, must file Form 8300. Any transactions conducted between a payer (or its agent) and the recipient in a
Keep a copy of each Form 8300 for 5 years from the date you file it.
Clerks of federal or state courts must file Form 8300 if more than $10,000 in cash is received as bail for an individual(s) charged with certain criminal offenses. For these purposes, a clerk includes the clerk’s office or any other office, department, division, branch, or unit of the court that is authorized to receive bail. If a person receives bail on behalf of a clerk, the clerk is treated as receiving the bail. See Item 33 under Part III, later.
If multiple payments are made in cash to satisfy bail and the initial payment does not exceed $10,000, the initial payment and subsequent payments must be aggregated and the information return must be filed by the 15th day after receipt of the payment that causes the aggregate amount to exceed $10,000 in cash. In such cases, the reporting requirement can be satisfied by sending a single written statement with the
aggregate Form 8300 amounts listed relating to that payer. Payments made to satisfy separate bail requirements are not required to be aggregated. See Treasury Regulations section
Casinos must file Form 8300 for nongaming activities (restaurants, shops, etc.).
Voluntary use of Form 8300. Form
8300 may be filed voluntarily for any suspicious transaction (see Definitions, later) for use by FinCEN and the IRS, even if the total amount does not exceed $10,000.
Exceptions. Cash is not required to be reported if it is received:
•By a financial institution required to file FinCEN Report 112, BSA Currency Transaction Report (BCTR);
•By a casino required to file (or exempt from filing) FinCEN Report 112, if the cash is received as part of its gaming business;
•By an agent who receives the cash from a principal, if the agent uses all of the cash within 15 days in a second transaction that is reportable on Form 8300 or on FinCEN Report 112, and discloses all the information necessary to complete Part II of Form 8300 or FinCEN Report 112 to the recipient of the cash in the second transaction;
•In a transaction occurring entirely outside the United States. See Publication 1544, Reporting Cash Payments of Over $10,000 (Received in a Trade or Business), regarding transactions occurring in Puerto Rico and territories and possessions of the United States; or
•In a transaction that is not in the course of a person’s trade or business.
When to file. File Form 8300 by the 15th day after the date the cash was received. If that date falls on a Saturday, Sunday, or legal holiday, file the form on the next business day.
Where to file. File the form with the Internal Revenue Service, Detroit Computing Center, P.O. Box 32621, Detroit, Ml 48232.
You may be able to
TIP electronically file Form 8300 using FinCEN's Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) Electronic Filing
Statement to be provided. You must give a written or electronic statement to each person named on a required Form 8300 on or before January 31 of the year following the calendar year in which the
cash is received. The statement must show the name, telephone number, and address of the information contact for the business, the aggregate amount of reportable cash received, and that the information was furnished to the IRS. Keep a copy of the statement for your records.
Multiple payments. If you receive more than one cash payment for a single transaction or for related transactions, you must report the multiple payments any time you receive a total amount that exceeds $10,000 within any
Taxpayer identification number (TIN). You must furnish the correct TIN of the person or persons from whom you receive the cash and, if applicable, the person or persons on whose behalf the transaction is being conducted. You may be subject to penalties for an incorrect or missing TIN.
The TIN for an individual (including a sole proprietorship) is the individual’s social security number (SSN). For certain resident aliens who are not eligible to get an SSN and nonresident aliens who are required to file tax returns, it is an IRS Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN). For other persons, including corporations, partnerships, and estates, it is the employer identification number (EIN).
If you have requested but are not able to get a TIN for one or more of the parties to a transaction within 15 days following the transaction, file the report and use the comments section on page 2 of the form to explain why the TIN is not included.
Exception. You are not required to provide the TIN of a person who is a nonresident alien individual or a foreign organization if that person or foreign organization:
•Does not have income effectively connected with the conduct of a U.S. trade or business;
•Does not have an office or place of business, or a fiscal or paying agent in the U.S.;
•Does not furnish a withholding certificate described in
(3) or
•Does not have to furnish a TIN on any return, statement, or other document as required by the income tax regulations under section 897 or 1445.
IRS Form 8300 (Rev. |
Page 4 |
FinCEN Form 8300 (Rev. |
Penalties. You may be subject to penalties if you fail to file a correct and complete Form 8300 on time and you cannot show that the failure was due to reasonable cause. You may also be subject to penalties if you fail to furnish timely a correct and complete statement to each person named in a required report. A minimum penalty of $25,000 may be imposed if the failure is due to an intentional or willful disregard of the cash reporting requirements.
Penalties may also be imposed for causing, or attempting to cause, a trade or business to fail to file a required report; for causing, or attempting to cause, a trade or business to file a required report containing a material omission or misstatement of fact; or for structuring, or attempting to structure, transactions to avoid the reporting requirements. These violations may also be subject to criminal prosecution which, upon conviction, may result in imprisonment of up to 5 years or fines of up to $250,000 for individuals and $500,000 for corporations or both.
Definitions
Cash. The term “cash” means the following.
•U.S. and foreign coin and currency received in any transaction; or
•A cashier’s check, money order, bank draft, or traveler’s check having a face amount of $10,000 or less that is received in a designated reporting transaction (defined below), or that is received in any transaction in which the recipient knows that the instrument is being used in an attempt to avoid the reporting of the transaction under either section 6050I or 31 U.S.C. 5331.
Note. Cash does not include a check drawn on the payer’s own account, such as a personal check, regardless of the amount.
Designated reporting transaction. A retail sale (or the receipt of funds by a broker or other intermediary in connection with a retail sale) of a consumer durable, a collectible, or a travel or entertainment activity.
Retail sale. Any sale (whether or not the sale is for resale or for any other purpose) made in the course of a trade or business if that trade or business principally consists of making sales to ultimate consumers.
Consumer durable. An item of tangible personal property of a type that, under ordinary usage, can reasonably be expected to remain useful for at least 1 year, and that has a sales price of more than $10,000.
Collectible. Any work of art, rug, antique, metal, gem, stamp, coin, etc.
Travel or entertainment activity. An item of travel or entertainment that pertains to a single trip or event if the combined sales price of the item and all other items relating to the same trip or event that are sold in the same transaction (or related transactions) exceeds $10,000.
Exceptions. A cashier’s check, money order, bank draft, or traveler’s check is not considered received in a designated reporting transaction if it constitutes the proceeds of a bank loan or if it is received as a payment on certain promissory notes, installment sales contracts, or down payment plans. See Publication 1544 for more information.
Person. An individual, corporation, partnership, trust, estate, association, or company.
Recipient. The person receiving the cash. Each branch or other unit of a person’s trade or business is considered a separate recipient unless the branch receiving the cash (or a central office linking the branches), knows or has reason to know the identity of payers making cash payments to other branches.
Transaction. Includes the purchase of property or services, the payment of debt, the exchange of cash for a negotiable instrument, and the receipt of cash to be held in escrow or trust. A single transaction may not be broken into multiple transactions to avoid reporting.
Suspicious transaction. A suspicious transaction is a transaction in which it appears that a person is attempting to cause Form 8300 not to be filed, or to file a false or incomplete form.
Specific Instructions
You must complete all parts. However, you may skip Part II if the individual named in Part I is conducting the transaction on his or her behalf only. For voluntary reporting of suspicious transactions, see Item 1, next.
Item 1. If you are amending a report, check box 1a. Complete the form in its entirety (Parts
To voluntarily report a suspicious transaction (see Suspicious transaction above), check box 1b. You may also telephone your local IRS Criminal Investigation Division or call the FinCEN Financial Institution Hotline at
Part I
Item 2. If two or more individuals conducted the transaction you are reporting, check the box and complete Part I on page 1 for any one of the individuals. Provide the same
information for the other individual(s) by completing Part I on page 2 of the form. If more than three individuals are involved, provide the same information in the comments section on page 2 of the form.
Item 6. Enter the taxpayer identification number (TIN) of the individual named. See Taxpayer identification number (TIN), earlier, for more information.
Item 8. Enter eight numerals for the date of birth of the individual named. For example, if the individual’s birth date is July 6, 1960, enter “07” “06” “1960.”
Item 13. Fully describe the nature of the occupation, profession, or business (for example, “plumber,” “attorney,” or “automobile dealer”). Do not use general or nondescriptive terms such as “businessman” or
Item 14. You must verify the name and address of the named individual(s). Verification must be made by examination of a document normally accepted as a means of identification when cashing checks (for example, a driver’s license, passport, alien registration card, or other official document). In item 14a, enter the type of document examined. In item 14b, identify the issuer of the document. In item 14c, enter the document’s number. For example, if the individual has a Utah driver’s license, enter “driver’s license” in item 14a, “Utah” in item 14b, and the number appearing on the license in item 14c.
Note. You must complete all three items (a, b, and c) in this line to make sure that Form 8300 will be processed correctly.
Part II
Item 15. If the transaction is being conducted on behalf of more than one person (including husband and wife or parent and child), check the box and complete Part II for any one of the persons. Provide the same information for the other person(s) by completing Part II on page 2. If more than three persons are involved, provide the same information in the comments section on page 2 of the form.
Items 16 through 19. If the person on whose behalf the transaction is being conducted is an individual, complete items 16, 17, and 18. Enter his or her TIN in item 19. If the individual is a sole proprietor and has an employer identification number (EIN), you must enter both the SSN and EIN in item 19. If the person is an organization, put its name as shown on required tax filings in item 16 and its EIN in item 19.
Item 20. If a sole proprietor or organization named in items 16 through 18 is doing business under a name other than that entered in item 16 (for example, a “trade” or “doing business as (DBA)” name), enter it here.

IRS Form 8300 (Rev. |
Page 5 |
FinCEN Form 8300 (Rev. |
Item 27. If the person is not required to furnish a TIN, complete this item. See Taxpayer identification number (TIN), earlier. Enter a description of the type of official document issued to that person in item 27a (for example, a “passport”), the country that issued the document in item 27b, and the document’s number in item 27c.
Note. You must complete all three items (a, b, and c) in this line to make sure that Form 8300 will be processed correctly.
Part III
Item 28. Enter the date you received the cash. If you received the cash in more than one payment, enter the date you received the payment that caused the combined amount to exceed $10,000. See Multiple payments, earlier, for more information.
Item 30. Check this box if the amount shown in item 29 was received in more than one payment (for example, as installment payments or payments on related transactions).
Item 31. Enter the total price of the property, services, amount of cash exchanged, etc. (for example, the total cost of a vehicle purchased, cost of catering service, exchange of currency) if different from the amount shown in item 29.
Item 32. Enter the dollar amount of each form of cash received. Show foreign currency amounts in U.S. dollar equivalent at a fair market rate of exchange available to the public. The sum of the amounts must equal item 29. For cashier’s check, money order, bank draft, or traveler’s check, provide the name of the issuer and the serial number of each instrument. Names of all issuers and all serial numbers involved must be provided. If necessary, provide this information in the comments section on page 2 of the form.
Item 33. Check the appropriate box(es) that describe the transaction. If the transaction is not specified in boxes
Part IV
Item 36. If you are a sole proprietorship, you must enter your SSN. If your business also has an EIN, you must provide the EIN as well. All other business entities must enter an EIN.
Item 41. Fully describe the nature of your business, for example, “attorney” or “jewelry dealer.” Do not use general or nondescriptive terms such as “business” or “store.”
Item 42. This form must be signed by an individual who has been authorized to do so for the business that received the cash.
Comments
Use this section to comment on or clarify anything you may have entered on any line in Parts I, II, III, and IV. For example, if you checked box b (Suspicious transaction) in line 1 above Part I, you may want to explain why you think that the cash transaction you are reporting on Form 8300 may be suspicious.
Privacy Act and Paperwork Reduction Act Notice. Except as otherwise noted, the information solicited on this form is required by the IRS and FinCEN in order to carry out the laws and regulations of the United States. Trades or businesses and clerks of federal and state criminal courts are required to provide the information to the IRS and FinCEN under section 6050I and 31 U.S.C. 5331, respectively. Section 6109 and 31 U.S.C. 5331 require that you provide your identification number. The principal purpose for collecting the information on this form is to maintain reports or records which have a high degree of usefulness in criminal, tax, or regulatory investigations or proceedings, or in the conduct of intelligence or
You are not required to provide information as to whether the reported transaction is deemed suspicious. Failure to provide all other requested information, or providing fraudulent information, may result in criminal prosecution and other penalties under 26 U.S.C. and 31 U.S.C.
Generally, tax returns and return information are confidential, as stated in section 6103. However, section 6103
allows or requires the IRS to disclose or give the information requested on this form to others as described in the Internal Revenue Code. For example, we may disclose your tax information to the Department of Justice, to enforce the tax laws, both civil and criminal, and to cities, states, the District of Columbia, and U.S. commonwealths and possessions, to carry out their tax laws. We may disclose this information to other persons as necessary to obtain information which we cannot get in any other way. We may disclose this information to federal, state, and local child support agencies; and to other federal agencies for the purposes of determining entitlement for benefits or the eligibility for and the repayment of loans. We may also provide the records to appropriate state, local, and foreign criminal law enforcement and regulatory personnel in the performance of their official duties. We may also disclose this information to other countries under a tax treaty, or to federal and state agencies to enforce federal nontax criminal laws and to combat terrorism. In addition, FinCEN may provide the information to those officials if they are conducting intelligence or
You are not required to provide the information requested on a form that is subject to the Paperwork Reduction Act unless the form displays a valid OMB control number. Books or records relating to a form or its instructions must be retained as long as their contents may become material in the administration of any law under 26 U.S.C. or 31 U.S.C.
The time needed to complete this form will vary depending on individual circumstances. The estimated average time is 21 minutes. If you have comments concerning the accuracy of this time estimate or suggestions for making this form simpler, we would be happy to hear from you. You can send us comments from www.irs.gov/ formspubs. Click on More Information and then click on Give us feedback. Or you can send your comments to Internal Revenue Service, Tax Forms and Publications Division, 1111 Constitution Ave. NW,
Other PDF Templates
Hair Salon Waiver Form Free - The waiver is designed to protect both the stylist and the salon in case of unforeseen outcomes.
To further clarify the process of ownership transfer, it is important to utilize a proper legal document, such as the Mobile Home Bill of Sale, which outlines the responsibilities and rights of both the buyer and the seller, ensuring transparency and compliance with Ohio regulations.
Roofing Warranty - Undergoing repairs by unauthorized individuals may jeopardize warranty validity.
Documents used along the form
The IRS Form 8300 is used to report cash payments exceeding $10,000 received in a trade or business. It is essential for maintaining compliance with federal regulations regarding large cash transactions. Alongside this form, several other documents may be relevant, depending on the specific circumstances of the transaction. Below is a list of forms and documents often used in conjunction with the IRS Form 8300.
- Form W-9: This form is used to request the taxpayer identification number (TIN) of a payee. It helps ensure that the information reported to the IRS is accurate.
- Form 1099-MISC: This form is issued to report payments made to independent contractors or other non-employees. It is often used when payments exceed a certain threshold.
- Form 1040: As the standard individual income tax return, this form may be relevant for individuals who receive large cash payments and need to report their income accurately.
- Form 941: This form is used by employers to report payroll taxes. If the cash payment involves wages, this form may be necessary for proper reporting.
- Form 1065: Partnerships use this form to report income, deductions, gains, and losses. It is relevant when the cash payment is made to or received from a partnership.
- Ohio Motor Vehicle Bill of Sale form: This important document is necessary when buying or selling a vehicle in Ohio, as it details the transaction and legally records the change of ownership. More information can be found at autobillofsaleform.com/ohio-motor-vehicle-bill-of-sale-form.
- Form 1120: Corporations use this form to report their income and expenses. It may be applicable if the cash transaction involves a corporate entity.
- Bank Statements: These documents provide a record of transactions and can help verify the source of the cash received, ensuring compliance with reporting requirements.
- Receipts and Invoices: Detailed records of the transactions can provide proof of the cash received and the purpose behind it. This documentation is crucial for accurate reporting and auditing purposes.
Understanding these documents can greatly assist in the proper handling of large cash transactions. Each form serves a unique purpose and contributes to maintaining transparency and compliance with IRS regulations. Keeping thorough records will help ensure that all obligations are met and can provide peace of mind in the event of an audit.
Similar forms
The IRS Form 8300 is designed to report cash payments exceeding $10,000 received in a trade or business. It plays a crucial role in combating money laundering and tax evasion. Similar to this form is the Currency Transaction Report (CTR), which financial institutions must file with the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN). The CTR serves to report transactions that involve cash deposits, withdrawals, or exchanges exceeding $10,000. Both documents aim to track large cash transactions, although the CTR is specific to financial institutions while the IRS Form 8300 pertains to businesses of all types.
Another document that parallels the IRS Form 8300 is the Report of Foreign Bank and Financial Accounts (FBAR). Individuals and entities with foreign accounts exceeding $10,000 must file this report annually. Like the IRS Form 8300, the FBAR is a tool used by the government to identify potential tax evasion and money laundering activities. Both forms require disclosure of significant financial transactions, although the FBAR focuses specifically on foreign accounts rather than cash transactions within the United States.
The Suspicious Activity Report (SAR) is also similar to the IRS Form 8300 in its intent to combat financial crimes. Financial institutions must file a SAR when they detect suspicious transactions that might indicate money laundering or fraud. While the IRS Form 8300 is mandatory for large cash transactions, the SAR is more subjective, allowing institutions to report any activity they deem suspicious, regardless of the amount. Both reports serve as vital tools for federal agencies in monitoring financial activities.
In the realm of real estate, the Form 1099-S comes into play. This form is used to report the sale or exchange of real estate, including cash transactions. When a property is sold for more than $10,000, the seller must file Form 1099-S, similar to how a business must file IRS Form 8300 for cash payments. Both documents help the IRS track significant financial transactions, ensuring that income is reported and taxes are paid accordingly.
The IRS Form 1042-S is another document that shares similarities with the IRS Form 8300. This form is used to report income paid to foreign persons, which may include cash payments exceeding certain thresholds. Both forms require the reporting of significant financial transactions, although Form 1042-S focuses specifically on payments to non-residents, while Form 8300 addresses cash transactions within the U.S. economy.
The Bank Secrecy Act (BSA) also aligns with the intent of the IRS Form 8300. The BSA requires financial institutions to report certain transactions that could signify money laundering or other financial crimes. While the IRS Form 8300 is specifically for cash transactions in a business context, the BSA encompasses a broader range of financial activities, reinforcing the government's commitment to monitoring and preventing illicit financial behavior.
In the context of tax compliance, the IRS Form W-2 serves a related purpose. Employers must report wages paid to employees, including any cash payments. While the IRS Form 8300 focuses on cash received by businesses, the W-2 ensures that all income, regardless of form, is reported to the IRS. Both forms are essential for maintaining transparency in financial transactions and ensuring tax compliance.
Another relevant document is the IRS Form 1098, which reports mortgage interest paid by individuals. If a homeowner pays more than $10,000 in mortgage interest, the lender must file this form. This reporting requirement shares a common goal with the IRS Form 8300: to ensure that significant financial transactions are documented and reported to the IRS, thereby facilitating accurate tax assessments.
When dealing with various financial forms, it's essential to ensure all necessary documentation is in order. For instance, the Georgia Power of Attorney form can be crucial for those needing to designate someone to manage their affairs, particularly in cases of incapacitation. Understanding the implications of such a document is important, and you can find more information about it at georgiapdf.com.
Lastly, the IRS Form 941, which is used to report employment taxes, also bears similarities to the IRS Form 8300. Employers must report income and payroll taxes withheld from employee wages, including any cash payments. While Form 941 focuses on payroll tax obligations, both forms highlight the importance of accurately reporting financial transactions to the IRS, contributing to overall tax compliance and transparency.
Dos and Don'ts
When filling out the IRS 8300 form, it is important to follow certain guidelines to ensure accuracy and compliance. Here are four things you should and shouldn't do:
- Do: Provide accurate information about the transaction, including the amount and the date.
- Do: Include your name, address, and taxpayer identification number.
- Don't: Leave any required fields blank; incomplete forms can lead to delays.
- Don't: Submit the form late; timely filing is essential to avoid penalties.
Key takeaways
Filling out the IRS 8300 form is an important process for businesses and individuals who receive large cash payments. Here are some key takeaways to consider:
- The IRS 8300 form is used to report cash transactions exceeding $10,000. This includes payments made in cash, cashier’s checks, or money orders.
- It must be filed within 15 days of receiving the cash payment. Timely submission helps avoid penalties.
- Providing accurate information is crucial. This includes details about the payer, the amount received, and the nature of the transaction.
- Failure to report can lead to significant penalties. The IRS takes cash transactions seriously, and non-compliance can result in fines.
- Keep a copy of the submitted form for your records. This serves as proof of compliance and can be useful for future reference.
Understanding these points can help ensure that you comply with IRS regulations when dealing with large cash transactions.
How to Use IRS 8300
Filling out the IRS 8300 form is an important step for businesses and individuals who receive cash payments over a certain threshold. Completing this form accurately ensures compliance with federal regulations. After you gather the necessary information, follow these steps to fill out the form correctly.
- Begin by downloading the IRS 8300 form from the official IRS website or obtain a physical copy.
- At the top of the form, enter your business name, address, and Employer Identification Number (EIN) or Social Security Number (SSN).
- Provide the date you received the cash payment.
- Fill in the amount of cash received. Be precise; accuracy is crucial.
- List the name, address, and taxpayer identification number (TIN) of the person or business from whom you received the cash.
- Indicate whether the payment was made on behalf of another person or entity.
- If applicable, include the name and address of the person or business for whom the cash was received.
- Complete the section regarding the nature of the transaction. Clearly describe what the payment was for.
- Sign and date the form to certify that the information provided is accurate and complete.
- Submit the form to the IRS. Make sure to keep a copy for your records.
Once the form is submitted, it is vital to maintain accurate records of the transaction. This will help in case of any future inquiries or audits. Stay informed about your responsibilities regarding cash transactions to ensure compliance and avoid penalties.
