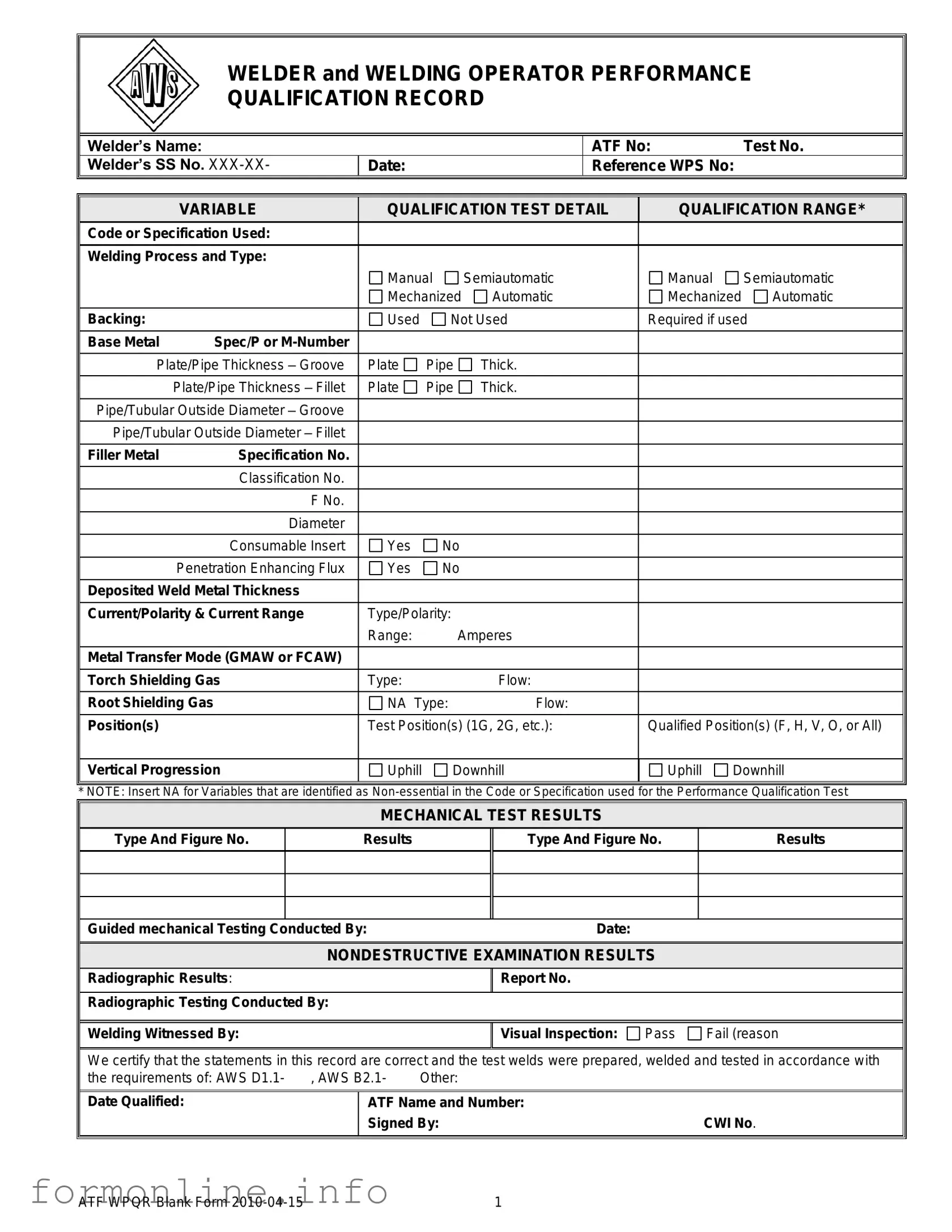
Fill Out a Valid Welder Performance Qualification Record Form
The Welder Performance Qualification Record (WPQR) form serves as a crucial document in the welding industry, ensuring that welders meet the necessary standards for various welding processes. This form captures essential information about the welder, including their name, identification numbers, and the specific test they completed. It outlines the details of the qualification test, such as the welding process used—whether manual, semiautomatic, or automatic—and the type of base metal involved. Additionally, it specifies important variables like plate thickness, filler metal specifications, and the positions in which the welder is qualified to work. Mechanical test results and non-destructive examination outcomes are also documented, providing a comprehensive overview of the welder’s capabilities. The form concludes with a certification section, affirming that all statements are accurate and that the tests were conducted in accordance with industry standards, such as AWS D1.1. By maintaining a clear and organized record, the WPQR not only verifies a welder's skills but also supports safety and quality in welding practices.
Common mistakes
-
Leaving the Welder’s Name section blank. Always ensure that the welder's name is clearly written at the top of the form.
-
Not including the ATF No and Test No. These numbers are crucial for tracking and verification purposes.
-
Failing to provide the WPS No. This number links the qualification to the specific welding procedure used.
-
Incorrectly marking the Welding Process and Type. Ensure that the correct method, whether manual or automatic, is selected.
-
Omitting details about the Base Metal Specification. Accurate information about the metal used is essential for qualification.
-
Not specifying the Filler Metal Specification and Classification No. This information is necessary for quality control.
-
Neglecting to fill out the Mechanical Test Results. This section must be completed to validate the performance qualification.
-
Forgetting to sign the form. A signature from the Certified Welding Inspector (CWI) is required for the record to be valid.
Preview - Welder Performance Qualification Record Form

WELDER and WELDING OPERATOR PERFORMANCE
QUALIFICATION RECORD
|
Welder’s Name: |
|
|
|
|
ATF No: |
|
Test No. |
||||||
|
Welder’s SS No. |
|
Date: |
|
|
Reference WPS No: |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
VARIABLE |
|
|
QUALIFICATION TEST DETAIL |
|
|
QUALIFICATION RANGE* |
|
|||||
|
Code or Specification Used: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Welding Process and Type: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
Manual |
Semiautomatic |
|
|
Manual |
|
Semiautomatic |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
Mechanized |
Automatic |
|
|
Mechanized |
Automatic |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
Backing: |
|
|
|
Used |
Not Used |
|
|
Required if used |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Base Metal |
Spec/P or |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Plate/Pipe Thickness – Groove |
|
Plate |
Pipe |
Thick. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
Plate/Pipe Thickness – Fillet |
|
Plate |
Pipe |
Thick. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Pipe/Tubular Outside Diameter – Groove |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Pipe/Tubular Outside Diameter – Fillet |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Filler Metal |
Specification No. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Classification No. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
F No. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Diameter |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Consumable Insert |
|
Yes |
No |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Penetration Enhancing Flux |
|
Yes |
No |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Deposited Weld Metal Thickness |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Current/Polarity & Current Range |
|
Type/Polarity: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
Range: |
Amperes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Metal Transfer Mode (GMAW or FCAW) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Torch Shielding Gas |
|
Type: |
|
Flow: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Root Shielding Gas |
|
NA Type: |
Flow: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Position(s) |
|
|
|
Test Position(s) (1G, 2G, etc.): |
|
|
Qualified Position(s) (F, H, V, O, or All) |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Vertical Progression |
|
Uphill |
Downhill |
|
|
Uphill |
Downhill |
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* NOTE: Insert NA for Variables that are identified as
|
|
|
|
MECHANICAL TEST RESULTS |
|
|
||
|
Type And Figure No. |
|
|
Results |
|
Type And Figure No. |
Results |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Guided mechanical Testing Conducted By: |
|
Date: |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NONDESTRUCTIVE EXAMINATION RESULTS |
|
|
|||
|
Radiographic Results: |
|
|
|
Report No. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Radiographic Testing Conducted By: |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Welding Witnessed By: |
|
|
|
Visual Inspection: Pass |
Fail (reason |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
We certify that the statements in this record are correct and the test welds were prepared, welded and tested in accordance with |
|||||||
|
the requirements of: AWS D1.1- |
, AWS B2.1- |
Other: |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Date Qualified: |
|
ATF Name and Number: |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
Signed By: |
CWI No. |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
ATF WPQR Blank Form |
|
|
1 |
|
|
|||
Other PDF Templates
Mvt 20-1 - Exemptions apply to certain vehicles, including those over 20 years old.
A Release of Liability form is a legal document where one party agrees not to hold another party responsible for any risks, injuries, or losses that may occur. This form is commonly used in events or activities that involve a certain level of risk. It ensures that individuals or entities are aware of and accept the potential dangers involved, and parties interested in utilizing this form can view and download the document for their needs.
Phone Insurance Claim - The form guides you through necessary claim information submission.
Documents used along the form
The Welder Performance Qualification Record (WPQR) is a critical document in the welding industry, serving to validate a welder's skills and abilities. Alongside the WPQR, several other forms and documents are commonly utilized to ensure comprehensive assessment and compliance with industry standards. Below is a list of these documents, each playing a vital role in the qualification process.
- Welding Procedure Specification (WPS): This document outlines the specific parameters and methods for welding a particular joint. It includes details such as material types, welding processes, and techniques to ensure consistency and quality in welds.
- Procedure Qualification Record (PQR): The PQR verifies that a specific welding procedure can produce a weld that meets the required standards. It documents the results of tests conducted on welds made using the WPS, ensuring the procedure's effectiveness.
- Welder Certification Card: This card serves as proof that a welder has successfully completed the necessary qualifications and is certified to perform welding tasks. It typically includes the welder’s name, certification number, and the types of welding they are qualified to perform.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) Report: An NDT report provides the results of tests conducted to evaluate the integrity of welds without causing damage. This may include methods like radiographic testing or ultrasonic testing, ensuring that any defects are identified early.
- New York Motorcycle Bill of Sale: A legal document that records the sale of a motorcycle, providing essential details about the transaction, including information about the buyer, seller, and the motorcycle itself. For more information, visit autobillofsaleform.com/motorcycle-bill-of-sale-form/new-york-motorcycle-bill-of-sale-form/.
- Inspection Report: This document records the findings of visual inspections conducted on welds. It includes details about the welds' appearance, dimensions, and any discrepancies found during the inspection process.
- Material Test Reports (MTR): MTRs provide documentation of the physical and chemical properties of the materials used in welding. This ensures that the materials meet specified standards and are suitable for the intended application.
- Calibration Certificates: These certificates confirm that the equipment used in the welding process has been calibrated according to industry standards. Proper calibration is essential for maintaining accuracy and consistency in welding operations.
In summary, the WPQR and its accompanying documents work together to create a robust framework for assessing welder qualifications and ensuring compliance with industry standards. Each document serves a unique purpose, contributing to the overall integrity and quality of welding practices.
Similar forms
The Welder Performance Qualification Record (WPQR) is closely related to the Welding Procedure Specification (WPS). The WPS outlines the specific parameters and procedures that a welder must follow to ensure a successful weld. It includes details such as the type of welding process, materials used, and the positions in which welding can occur. Both documents serve as essential references; the WPS provides the guidelines, while the WPQR demonstrates that the welder has the necessary skills to adhere to those guidelines effectively.
In navigating the complexities of legal documents, understanding the significance of the General Power of Attorney form can be crucial for ensuring that your wishes are respected. Similar to the various qualifications and specifications required in welding, this form allows individuals to grant trusted agents the power to make important decisions on their behalf when they are unable to do so. For those looking to facilitate this process, additional resources and guidance can be found at https://georgiapdf.com.
Another document similar to the WPQR is the Procedure Qualification Record (PQR). The PQR is a record that verifies the welding procedure's effectiveness through testing. It details the variables used during welding and the results of mechanical tests performed on the welds. While the WPQR focuses on the qualifications of the welder, the PQR emphasizes the validity of the welding procedure itself, ensuring that it meets the required standards.
The Certificate of Qualification is also akin to the WPQR. This document serves as proof that a welder has successfully completed the necessary qualifications and tests to perform specific types of welding. It typically includes the welder's name, the types of welding they are qualified for, and the date of qualification. While the WPQR provides a detailed record of the performance test, the Certificate of Qualification is a concise summary affirming the welder's credentials.
The Welding Inspection Report (WIR) shares similarities with the WPQR as well. The WIR documents the findings of inspections conducted during the welding process. It includes information about the quality of the welds and any issues that may have arisen. Both documents aim to ensure that the welding work meets industry standards, but the WIR focuses more on the inspection results rather than the qualifications of the welder.
The Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) Report is another document that relates to the WPQR. This report details the results of testing methods used to evaluate the integrity of welds without causing damage. Techniques such as radiography or ultrasonic testing are often included. While the WPQR certifies the welder's skills, the NDT Report assesses the quality of the welds produced, making both documents crucial for maintaining high standards in welding practices.
The Weld Map is a document that can be compared to the WPQR in terms of tracking and documenting welds. It provides a visual representation of the welds made on a project, including their locations and specifications. This document assists in quality control and inspection processes. While the WPQR focuses on the qualifications of the welder, the Weld Map helps ensure that the work aligns with the established welding procedures.
Lastly, the Welder’s Log is similar to the WPQR as it records the welder’s ongoing qualifications and experience. This log includes details about the types of welding performed, materials used, and any certifications obtained over time. While the WPQR captures a specific qualification test, the Welder’s Log provides a broader view of the welder’s skills and development throughout their career.
Dos and Don'ts
When filling out the Welder Performance Qualification Record form, attention to detail is crucial. Here’s a list of things you should and shouldn't do to ensure accuracy and compliance.
- Do: Provide accurate personal information, including the welder’s name and Social Security number.
- Do: Use the correct reference WPS number to ensure consistency with the welding procedure specification.
- Do: Clearly indicate the type of welding process used, whether manual, semiautomatic, or automatic.
- Do: Include all relevant mechanical test results and non-destructive examination results.
- Do: Sign the form to certify that the information provided is correct and complete.
- Don't: Leave any sections blank; if a variable is not applicable, indicate it with "NA."
- Don't: Use outdated codes or specifications; always refer to the most current standards.
Following these guidelines will help ensure that your Welder Performance Qualification Record is filled out correctly, facilitating a smoother qualification process.
Key takeaways
Filling out the Welder Performance Qualification Record form is a crucial step in ensuring compliance and competency in welding practices. Below are key takeaways to consider:
- Accurate Information: Ensure that all personal details, including the welder's name and identification numbers, are filled out correctly to avoid any discrepancies.
- Reference WPS Number: Always include the relevant Welding Procedure Specification (WPS) number, as it serves as a guide for the welding process used.
- Qualification Range: Clearly indicate the qualification range for variables such as base metal thickness and filler metal specifications. This information is essential for understanding the scope of the welder's qualifications.
- Mechanical Test Results: Document the results of any mechanical tests conducted. This data is critical in assessing the welder's performance and adherence to standards.
- Non-Destructive Examination: Include results from any non-destructive testing, such as radiographic tests. This information provides insight into the quality of the welds.
- Signature and Certification: The form must be signed by a qualified individual, confirming that the information provided is accurate and that the tests were performed according to the specified requirements.
- Test Positions: Specify the test positions, such as 1G or 2G, and indicate whether the welder is qualified for vertical, overhead, or other positions.
- Visual Inspection Results: Clearly state the results of the visual inspection, including any reasons for failure if applicable. This information is vital for quality assurance.
- Documentation Retention: Keep a copy of the completed form in a secure location. This record serves as a reference for future qualifications and compliance checks.
Understanding these key points will aid in the proper completion and utilization of the Welder Performance Qualification Record form, ultimately supporting quality welding practices.
How to Use Welder Performance Qualification Record
Filling out the Welder Performance Qualification Record form is essential for documenting a welder's skills and qualifications. This record serves as proof of competency and is often required for compliance with industry standards. Follow these steps carefully to ensure all necessary information is accurately captured.
- Welder’s Name: Write the full name of the welder.
- ATF No: Enter the ATF number associated with the welder.
- Test No: Fill in the specific test number for this qualification.
- Welder’s SS No: Provide the welder's Social Security Number in the format XXX-XX-XXXX.
- Date: Record the date when the qualification test was conducted.
- Reference WPS No: Indicate the Welding Procedure Specification number referenced for this qualification.
- Code or Specification Used: Specify the code or standard that applies to the qualification.
- Welding Process and Type: Check the appropriate box for the welding process used (e.g., Manual, Semiautomatic, etc.).
- Backing: Indicate whether backing was used, not used, or required if used.
- Base Metal Spec/P or M-Number: Enter the specification or material number of the base metal.
- Plate/Pipe Thickness: Fill in the thickness for both groove and fillet welds.
- Pipe/Tubular Outside Diameter: Specify the outside diameter for both groove and fillet welds.
- Filler Metal Specification No: Provide the specification number for the filler metal used.
- Classification No: Enter the classification number for the filler metal.
- F No.: Write the F number associated with the filler metal.
- Diameter: Indicate the diameter of the filler metal.
- Consumable Insert: Check yes or no if a consumable insert was used.
- PENETRATION ENHANCING FLUX: Check yes or no if this was used.
- Deposited Weld Metal Thickness: Fill in the thickness of the deposited weld metal.
- Current/Polarity & Current Range: Specify the type and range of current used.
- Metal Transfer Mode: Indicate the mode used (e.g., GMAW or FCAW).
- Torch Shielding Gas: Provide the type and flow rate of the shielding gas.
- Root Shielding Gas: Specify the type and flow rate of the root shielding gas, if applicable.
- Test Position(s): List the test positions (e.g., 1G, 2G, etc.).
- Qualified Position(s): Indicate the qualified positions (e.g., F, H, V, O, or All).
- Vertical Progression: Check either uphill or downhill based on the welding technique used.
- MECHANICAL TEST RESULTS: Document the results of any mechanical tests conducted.
- NONDESTRUCTIVE EXAMINATION RESULTS: Provide details of the radiographic results and report number.
- Welding Witnessed By: Include the name of the individual who witnessed the welding.
- Visual Inspection: State whether the inspection passed or failed, along with the reason if it failed.
- Certification: Sign and date the record, including the CWI number and ATF name and number.